Tea, a beloved beverage ingrained deeply in cultures worldwide, serves as more than just a drink—it is an emblem of comfort, tradition, and social connection. In India particularly, tea holds a revered status, transcending its role as a mere refreshment to become a cornerstone of daily life. However, a debate persists regarding the practice of adding milk to tea and its potential implications on health. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the multifaceted aspects of this debate, drawing insights from experts to uncover the truth behind the impact of milk in tea.
Benefits of Tea:
Before delving into the effects of adding milk to tea, it's crucial to understand the inherent benefits of tea itself. Both green tea and black tea contain a myriad of bioactive compounds, including catechins, EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate), and polyphenols. These compounds are renowned for their antioxidant properties, which help combat oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. Additionally, tea consumption has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases, such as cancer, cardiovascular ailments, and neurodegenerative disorders. Moreover, tea is known to promote the proliferation of stem cells, contributing to cellular regeneration and potentially slowing down the aging process.
Black Tea's Health Benefits:
While green tea often takes the spotlight for its perceived health benefits, black tea boasts its own array of advantageous properties. Despite undergoing fermentation, black tea retains a significant portion of its polyphenol content, thereby conferring similar health benefits as its green counterpart. Research suggests that black tea consumption may aid in cardiovascular health, improve gut microbiota, and enhance cognitive function. Moreover, the presence of theaflavins and thearubigins in black tea contributes to its unique flavor profile and potential health-promoting effects.
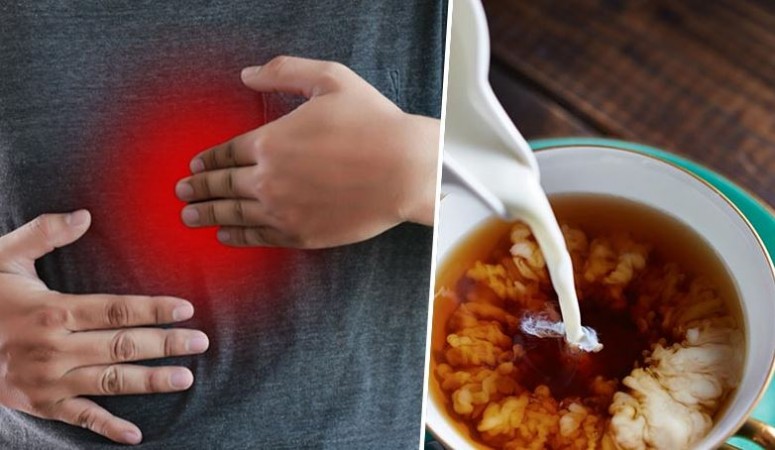
Drawbacks of Adding Milk to Tea:
One of the most hotly debated topics surrounding tea consumption pertains to the practice of adding milk. While milk is commonly used to enhance the taste and creaminess of tea, its interaction with tea compounds raises concerns among health enthusiasts and experts alike. When milk is added to tea, the casein proteins in milk can bind to catechins, thereby reducing their bioavailability. Additionally, the fat content in milk can form insoluble complexes with tea polyphenols, hindering their absorption in the body. Consequently, the purported health benefits of tea may be compromised when consumed with milk.
Mixing Different Types of Tea:
In the quest for flavor diversity and enhanced nutritional benefits, individuals often experiment with mixing different types of tea. While this practice may yield intriguing flavor profiles, its impact on the bioavailability of tea compounds warrants closer examination. When combining various teas, such as green tea, black tea, or herbal infusions, the interaction between their respective bioactive constituents may influence their absorption and metabolic fate in the body. Therefore, while mixing teas can be a delightful culinary endeavor, its implications on health outcomes remain a subject of interest for researchers and consumers alike.
Strategies for Optimal Tea Consumption:
Given the complexities surrounding tea consumption and the addition of milk, several strategies can be adopted to maximize the health benefits derived from tea. Firstly, consuming tea without added sugar and milk ensures the preservation of its natural bioactive compounds and antioxidant properties. Furthermore, selecting high-quality teas sourced from reputable producers can ensure optimal flavor and nutritional content. For those who enjoy the creaminess of milk in their tea, opting for plant-based milk alternatives or minimizing the quantity of milk added can mitigate potential interference with tea polyphenols. Additionally, exploring diverse tea varieties and blends can provide a spectrum of flavors and health-promoting compounds, catering to individual preferences and nutritional needs.
In conclusion, the debate surrounding the addition of milk to tea reflects the intricate interplay between culinary traditions, taste preferences, and health considerations. While tea itself offers a plethora of health benefits, the inclusion of milk may pose challenges in maximizing the bioavailability of its bioactive compounds. By understanding the nuances of tea composition and adopting informed consumption practices, individuals can strike a balance between flavor enjoyment and health optimization. Ultimately, tea remains a versatile beverage that continues to captivate enthusiasts worldwide, offering a blend of cultural significance and wellness potential.
If you also shrink your nose and mouth after seeing mushroom, then know its benefits
Want to Reduce Belly Fat? Take THESE nuts daily
Do not ignore the prick in the chest, there can be 5 dangerous reasons