What is chickenpox and where does it come from
Chickenpox (also known as chicken pox) is an infectious disease.Chickenpox (Varicella). It is caused by the Varicella Zoster virus. By the way, a close relative of a friend of many herpes.
All herpes are contagious, but the varicella is the coolest. Chickenpox is spread by airborne droplets, and it does this very actively. To catch the infection, it is sometimes enough for a second to look into the room of the patient.
It always seemed to people that the sore was literally carried by air, by wind. Hence the first part of the name - wind. The smallpox was called because of the numerous eruptions in the form of bubbles filled with liquid (papules), similar to those formed with smallpox.
Fortunately, chickenpox is not so lethal.
What is dangerous chickenpox for children and adults?
First of all, the volatility. The contagiousness of the varicella is so high that the chickenpox has long been considered a purely pediatric disease: the child had almost no chance to grow up without meeting the infection. Fortunately, most people at the age of 1–12 years old can get chicken pox easily, and having been ill, they acquire immunity for the rest of their lives.
But sometimes a disease can cause serious complications. Chickenpox:
But before you are afraid of complications, you should make sure that it is about chickenpox.
What are the symptoms of chickenpox in children and adults?
At the initial stage, it is almost impossible to recognize the disease. In chickenpox, there is a long incubation period: 2-3 weeks after infection, the virus doesn’t make itself felt. Its first manifestations are similar to the flu:
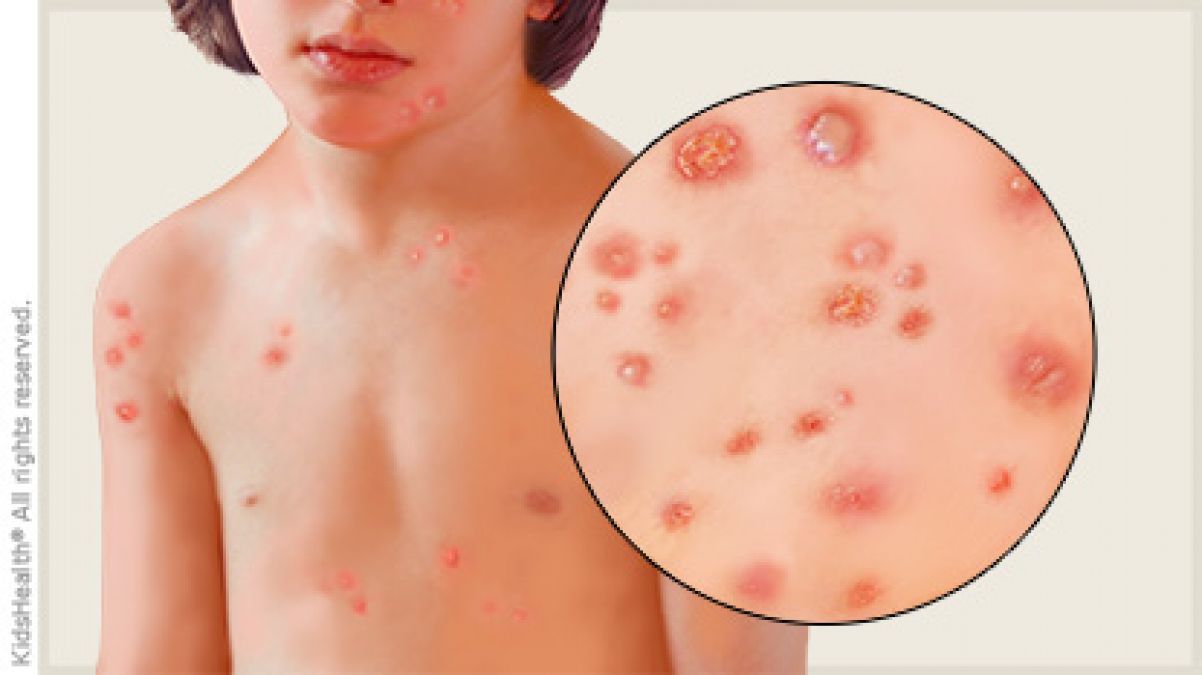
However, these symptoms are not required. Quite often, small red dots immediately appear on the skin. At first they resemble mosquito bites, but within a few hours they turn into bubbles filled with turbid liquid.
The rash spreads throughout the body, sometimes capturing even the oral mucosa and genitals.
After a day or two, the bubbles burst, their contents leak. Ospinki dry up and soon fall off, leaving no traces. But next to the disappeared new ones appear.
The rash lasts 4–8 days. All this time a person remains infectious, although he feels well already: the temperature and discomfort pass a maximum on the fourth day after the onset of the active stage of the disease.
This happens with light or normal flow of chickenpox. But there are other situations.
When you need to see a doctor urgently or call an ambulance
Complications most often occur in those who are more or less 1-12 years old, as well as in people with weakened immunity . To reduce the risks, you need qualified medical assistance.
As soon as possible, consult with your doctor if you are ill:
How to treat chickenpox
Chickenpox is a virus. And, as with most viruses, there is no specific treatment for it. Helping a sick person is reduced only to reliefWhat you need to know about chickenpox major symptoms.
Fever and headache
Remember: paracetamol and nothing else! Popular painkillers and antipyretics based on ibuprofen should not be taken. According to some sourcesIt has been shown that a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug can be used in patients with varicella or zoster disease., ibuprofen with chickenpox increases the frequency of complications in the form of skin infections.
Aspirin is contraindicated. In conjunction with the varicella-zoster virus, it has a powerful toxic effect on the liver and brain (the so-called Ray's syndromeReye's syndrome).
Itching
To relieve itching, the therapist may recommend an antihistamine to you. Given the cunning of the virus, in no case do not assign it yourself!
You can also treat the skin lotion with callamine according to the instructions.
Scratches and wounds
In order not to scratch the skin and not infect the wound:
Cut the nails as short as possible. If the baby is sick, put on thin protective gloves.
Wear clean loose clothing.
Change bed and underwear often.
It is not necessary to smear the rash with a brilliant green: brilliant green will not speed up the ripening period of the bubbles. Color is what helps mark pimples in order to track the moment when new ones stop appearing.
Sore mouth
If there are rashes and on the mucous of the mouth, doctors recommend eating ice cream without sugar. The cold will help relieve discomfort. Also try not to eat salty and spicy foods.
Possible complications
If chickenpox can be dangerous for you, your doctor will prescribe medications that can help you reduce the duration of the disease and reduce the risk of complications. It may be an antiviral agent, such as acyclovir, or an immunoglobulin for intravenous administration. True, they will be effective only if used in the first 24 hours after the rash appears.
If it comes to complications, serious means are used. Depending on which organ is affected, your doctor will prescribe antibiotics and more powerful antiviral drugs. You may have to go to the hospital.