Understanding the distribution of fat in different body parts is crucial for effective weight management. Various hormones play a significant role in where and how fat is stored in the body. By identifying and managing these hormonal imbalances, you can better target specific areas of fat accumulation. Here’s a detailed look at how different hormones affect fat distribution and what you can do to manage them:
1. Abdominal Fat
Hormonal Influence:
Abdominal fat, especially around the upper part of the stomach, is often linked to hormonal imbalances involving cortisol and insulin. Cortisol, known as the stress hormone, can become elevated due to chronic stress, leading to increased fat storage in the abdominal area. Insulin resistance, where the body does not respond effectively to insulin, can also contribute to abdominal fat accumulation.
Management Strategies:
Stress Reduction: Practice stress-relieving activities like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to lower cortisol levels.
Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit sugar and refined carbohydrates to manage insulin levels.
Regular Exercise: Engage in a combination of cardiovascular exercise and strength training to help reduce abdominal fat.
2. Chest Fat in Men
Hormonal Influence:
Men may experience fat accumulation in the chest area, a condition sometimes referred to as gynecomastia, due to elevated estrogen levels. Estrogen is typically considered a female hormone but is present in lower levels in men. An imbalance where estrogen levels are too high can lead to fat deposits in the chest.
Management Strategies:
Hormone Testing: Consult with a healthcare provider to check hormone levels and determine if any treatment is needed.
Strength Training: Incorporate chest exercises like push-ups and bench presses to strengthen and tone the chest muscles.
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet and avoid excessive alcohol consumption, which can affect estrogen levels.
3. Face Fat
Hormonal Influence:
Excess fat in the face can be attributed to high levels of cortisol, insulin resistance, and conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) in women. Elevated cortisol and insulin levels can lead to fat accumulation in the face, making it appear fuller and rounder.
Management Strategies:
Balanced Diet: Adopt a diet low in sugar and high in fiber and antioxidants to help manage insulin levels and support overall health.
Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help reduce water retention and puffiness in the face.
Facial Exercises: Engage in facial exercises and massages to tone facial muscles and improve circulation.
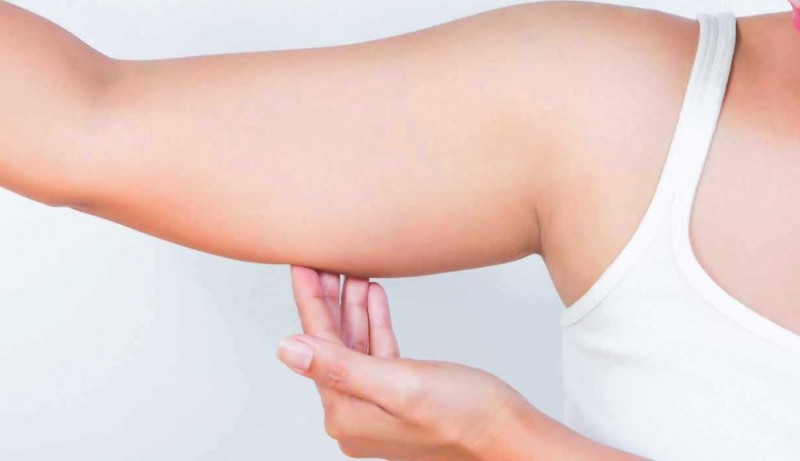
4. Upper Body Fat
Hormonal Influence:
Excess fat in the upper body, including the arms, back, and neck, can be related to an imbalance in androgen hormones. Androgens are typically male hormones but are present in both genders. An imbalance can lead to increased fat deposits in these areas.
Management Strategies:
Healthy Fats: Incorporate foods rich in polyunsaturated fats, like walnuts and almonds, to help balance hormone levels.
Strength Training: Focus on upper body workouts to build muscle and reduce fat in the arms, back, and neck.
Regular Cardio: Engage in regular cardiovascular exercises to help burn fat throughout the upper body.
5. Hip and Thigh Fat
Hormonal Influence:
Fat accumulation in the hips and thighs is often associated with high estrogen levels. Estrogen promotes fat storage in these areas, which is why women commonly store fat in their hips and thighs.
Management Strategies:
Protein Intake: Increase protein intake to support muscle growth and fat loss in the lower body.
Strength Training: Perform lower body exercises like squats and lunges to tone and strengthen the hips and thighs.
Stress Management: Manage stress effectively, as chronic stress can disrupt hormone balance and contribute to fat accumulation.
General Tips for Hormonal Balance and Fat Management
Consult a Professional: Regularly consult with healthcare professionals to check hormone levels and address any imbalances.
Healthy Lifestyle: Maintain a balanced diet, regular exercise routine, and adequate sleep to support overall hormonal health.
Avoid Excessive Stress: Practice stress management techniques to keep cortisol levels in check.
By understanding the role of different hormones in fat distribution and adopting targeted strategies, you can effectively manage and reduce fat in specific areas of your body.
6 Quick and Healthy Breakfast Ideas for a Busy Morning
Israel Orders Evacuation of Humanitarian Zone in Gaza
National Milk Chocolate Day – July 28! Indulge in These Irresistible Milk Chocolates