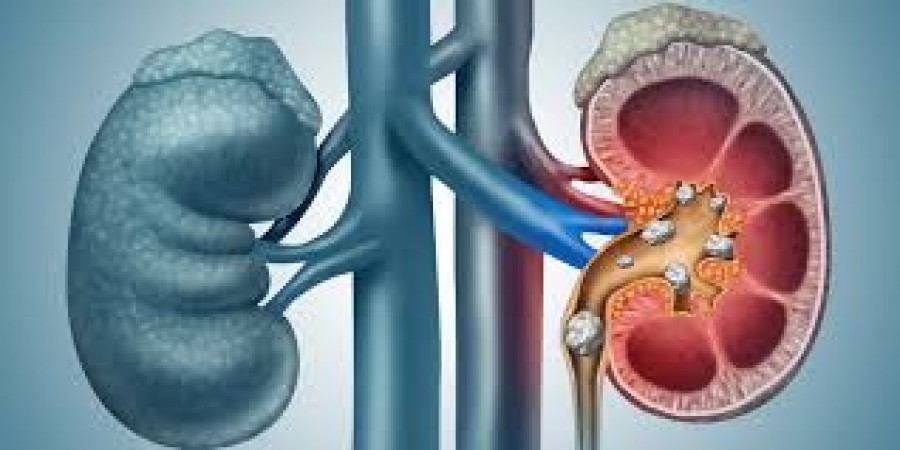
Body stones, medically known as calculi, are solid formations that occur in various parts of the body. They can develop in the kidneys, gallbladder, bladder, and other areas. These stones are formed from minerals and salts and can cause significant discomfort and health issues if not addressed.
Types of Body Stones
- Kidney Stones: These form in the kidneys and can travel through the urinary tract.
- Gallstones: These form in the gallbladder and can block bile ducts.
- Bladder Stones: These develop in the bladder, often due to urinary tract infections or bladder inflammation.
- Other Stones: Less common stones can form in the pancreas or salivary glands.
Symptoms of Kidney Stones
Pain and Discomfort
The most common symptom of kidney stones is intense pain. This pain often begins in the back or side, just below the ribs, and can radiate to the lower abdomen and groin. The pain can come in waves and vary in intensity.
Changes in Urination
- Frequent Urination: A frequent need to urinate, often in small amounts.
- Painful Urination: A burning sensation or severe pain during urination.
- Discolored Urine: Urine may appear pink, red, or brown, indicating blood.
Other Symptoms
- Nausea and Vomiting: Often due to the body's reaction to severe pain.
- Fever and Chills: These can occur if an infection is present.
Identifying Gallstones
Abdominal Pain
Gallstones often cause severe pain in the upper right abdomen, just below the rib cage. This pain can extend to the back or right shoulder and usually occurs after eating fatty meals.
Digestive Issues
- Indigestion: Bloating, gas, and indigestion can be signs of gallstones.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Similar to kidney stones, gallstones can also cause nausea.
Jaundice
- Yellowing of Skin and Eyes: This occurs if a stone blocks the bile duct, causing bile to build up in the liver.
Bladder Stones Symptoms
Urination Problems
- Frequent and Painful Urination: A constant need to urinate with discomfort.
- Blood in Urine: Hematuria, or blood in the urine, can be a sign.
Lower Abdominal Pain
Pain in the lower abdomen or pelvic area is common with bladder stones.
Diagnosis of Body Stones
Medical History and Physical Examination
Doctors start with a thorough medical history and physical examination to identify symptoms and possible causes.
Imaging Tests
- X-rays: Used to visualize stones in the urinary or biliary tract.
- Ultrasound: A non-invasive method to detect stones in kidneys, gallbladder, and bladder.
- CT Scans: Provide detailed images to locate and size stones accurately.
Laboratory Tests
- Urine Tests: To check for blood, infection, or crystals in the urine.
- Blood Tests: To assess kidney function and detect any infections.
Risk Factors for Developing Stones
Dietary Habits
- High Salt and Protein Intake: Can increase the risk of kidney stones.
- Low Fluid Intake: Dehydration is a significant risk factor for all types of stones.
Medical Conditions
- Obesity: Increases the risk of gallstones and kidney stones.
- Diabetes: Affects metabolic processes, leading to stone formation.
Family History
A family history of stones can increase your risk, suggesting a genetic predisposition.
Preventing Stones in the Body
Hydration
- Drink Plenty of Water: Staying well-hydrated helps prevent stone formation.
- Limit Sugary and Caffeinated Beverages: These can contribute to dehydration.
Diet Modifications
- Reduce Salt Intake: Too much salt can lead to the formation of stones.
- Balance Calcium Intake: Too much or too little calcium can contribute to stones.
Regular Check-Ups
- Routine Medical Exams: Regular check-ups can catch early signs of stone formation.
- Monitor Chronic Conditions: Keeping conditions like diabetes and hypertension under control can reduce risks.
Treatment Options
Medications
- Pain Relievers: To manage the discomfort associated with stones.
- Alpha Blockers: Help relax muscles in the ureter to pass kidney stones more easily.
- Bile Acids: Used to dissolve gallstones in some cases.
Surgical Interventions
- Shock Wave Lithotripsy: Uses sound waves to break kidney stones into smaller pieces.
- Ureteroscopy: A scope is used to remove or break up stones in the urinary tract.
- Cholecystectomy: Surgical removal of the gallbladder to treat gallstones.
Home Remedies
- Hydration: Drinking water and lemon juice can help pass small kidney stones.
- Diet Adjustments: Reducing oxalate-rich foods for kidney stones and fatty foods for gallstones.
When to See a Doctor
Severe Pain
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe pain that you cannot manage with over-the-counter pain relievers.
Persistent Symptoms
If symptoms persist despite home remedies or lifestyle changes, consult a healthcare professional.
Signs of Infection
Fever, chills, or other signs of infection require prompt medical attention to prevent complications.
Understanding the Long-Term Outlook
Managing Recurrence
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthier diet and staying hydrated can prevent recurrence.
- Regular Monitoring: Routine check-ups with imaging tests can catch stones early.
Living with Stones
While living with body stones can be challenging, understanding your risk factors and symptoms can help manage the condition effectively.
Kapil Sibal Elected President of Supreme Court Bar Association
Opportunity to earn lakhs of rupees by playing BGMI: The winner of this new tournament will get ₹ 25,00,000!
These powerful bikes and scooters will hit the Indian market, know when they can be launched