A breakthrough development emerging from the laboratories of IIT Delhi showcases a pioneering method to enhance the scratch resistance of glass surfaces by integrating an atomically thin graphene layer. This innovative approach capitalizes on the inherent traits of glass—its rigidity and slippery nature—to significantly bolster its scratch resistance.
The study, spearheaded by researchers at IIT Delhi, introduces a straightforward technique to create ultra-scratch-resistant glass by applying an extremely thin coating of graphene. The incorporation of this graphene layer seamlessly integrates into current manufacturing processes for consumer electronics. This advancement holds substantial promise for augmenting the longevity and durability of next-generation smartphones and tablets.
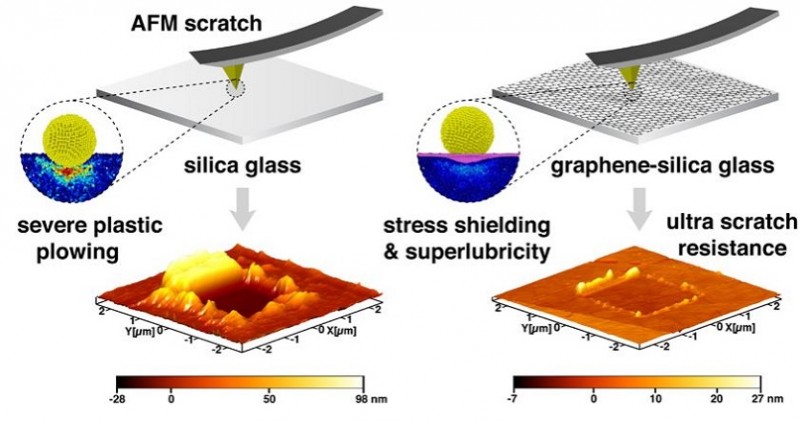
The primary goal of the researchers was to tackle the longstanding challenge of making glass surfaces scratch-proof, a feat previously deemed unattainable. Over time, smartphones and similar devices accumulate scratches, which not only compromise their structural integrity but also diminish the user experience by adversely affecting the optical clarity of the glass. Scratched glass is notably less transparent than its unblemished counterpart.
In rigorous tests conducted by the IIT Delhi team, the graphene-coated glass surfaces exhibited an outstanding 98% reduction in friction forces compared to bare silicon glass under multiple loads. Rather than offering resistance and succumbing to scratches upon contact with other surfaces or objects, the graphene-infused glass smoothly glides, preventing damage.
The findings of this groundbreaking research have been detailed in a paper published in ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces. Nitya Nand Gosvami, one of the study's authors, highlighted, "Nanoscale scratch experiments conducted on silica glass surfaces using hard diamond probes revealed that the graphene coating effectively transforms the glass surface into an exceptionally smooth, ultra-low friction surface—reaching the realms of 'superlubricity'. Additionally, the load-bearing capacity of graphene acts as a protective shield, safeguarding the underlying glass from applied pressure, thereby minimizing damage from abrasive forces to minuscule surface depressions."
Graphene layers, one millionth the thickness of a single strand of human hair, have proven through computational models to serve as a resilient shield for glass, affirming their potential to revolutionize scratch resistance technology.
Realme's Dual-Platform Strategy Triumphs: Narzo N53 Emerges as Q3 2023 Bestseller on Amazon