Washington: NASA has released two captivating images of Mars, captured by the MAVEN spacecraft using ultraviolet wavelengths. By examining Mars in these wavelengths, scientists gain valuable insights into the planet's atmospheric composition and surface characteristics.
Studying Mars's atmosphere is crucial in determining its habitability, and MAVEN is specifically designed for this purpose. The mission focuses on exploring the upper atmosphere, ionosphere, and their interactions with the Sun and solar wind. MAVEN will celebrate a decade of operations in September 2024, marking a significant milestone in our understanding of the Red Planet.
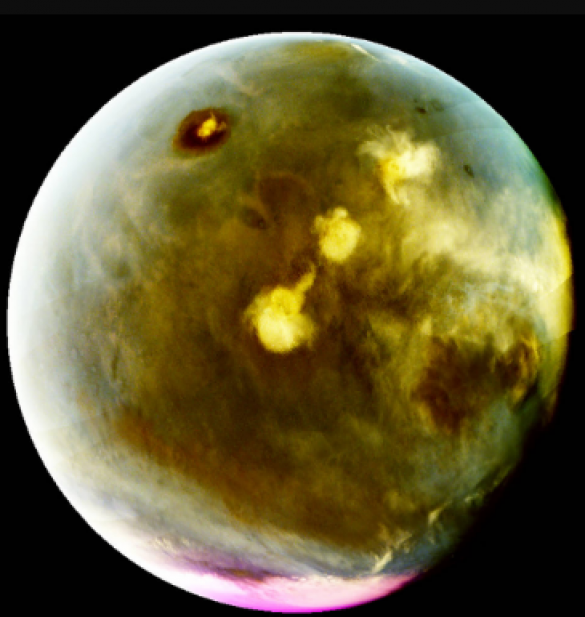
To make the images visible to the human eye, they have been color adjusted from their original ultraviolet form. Mars's surface is represented in tan or green hues, depending on the image processing techniques employed. The purple patches indicate the presence of atmospheric ozone, while clouds and hazes appear in various shades of white or blue.
Also Read: Xiaomi Launched New Xiaomi Pad 6 2023: A Powerful Android Tablet with Enhanced Features
One of the images displays the southern hemisphere of Mars during its summer season, characterized by the planet's proximity to the Sun. Similar to Earth, Mars experiences seasons due to its tilt. The "southern polar ice cap" is visible in white at the bottom of the image, appearing to melt under the influence of the summer heat.
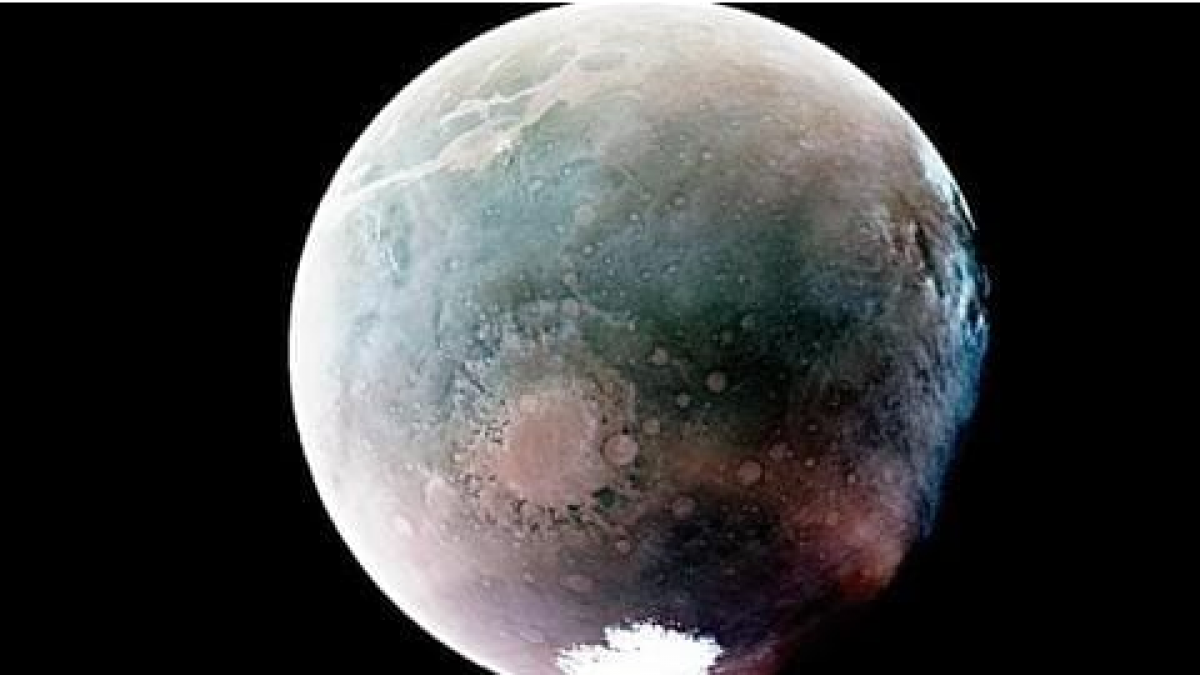

Several fascinating features stand out in the 'summer' image of Mars. In the bottom left corner, the Argyre Basin, one of the deepest craters on Mars spanning over 1,200km wide, is seen. The crater is filled with atmospheric haze, portrayed in delicate shades of pale pink. At the top left, a vast canyon system named Valles Marineris is depicted in tan.
Also Read: Xiaomi Launched New Xiaomi Pad 6 2023: A Powerful Android Tablet with Enhanced Features

The second image captures Mars's northern hemisphere as the planet reaches the farthest point in its orbit from the Sun. The bright magenta region indicates atmospheric ozone, while thick clouds appear as white formations in the northern polar region. Once again, the distinctive Valles Marineris canyons are visible, this time in tan shades at the lower left of the image.