Brain aneurysms are a complex medical condition that can have severe consequences if left untreated. In this article, we will delve into the various aspects of brain aneurysms, including their diagnosis and treatment options, in simple and easy-to-understand language.
A brain aneurysm, also known as a cerebral aneurysm or intracranial aneurysm, is a weak or bulging spot in an artery within the brain. Think of it like a balloon that has developed a weak spot, making it susceptible to rupture.
There are two primary types of brain aneurysms:
Saccular aneurysms are the most common type and have a rounded or sac-like shape. They often form at the branching points of arteries within the brain.
Fusiform aneurysms are less common and involve the entire circumference of the blood vessel. They appear elongated and spindle-shaped.
Understanding the causes and risk factors associated with brain aneurysms is crucial.
The exact cause of brain aneurysms is not always clear, but several factors may contribute:
A family history of aneurysms can increase your risk.
Hypertension can weaken blood vessel walls, making them more prone to aneurysm formation.
Tobacco use is a significant risk factor, as it can damage blood vessels over time.
Certain factors may increase your risk of developing a brain aneurysm:
Aneurysms are more common in individuals over the age of 40.
Women are more likely than men to develop aneurysms.
Recognizing the symptoms of a brain aneurysm is essential for early diagnosis and treatment.
A sudden, excruciating headache is often described as the worst headache of one's life.
Nausea and vomiting may accompany the intense headache.
Blurred or double vision can occur due to pressure on the optic nerve.
A stiff neck and neck pain are common symptoms.
A ruptured brain aneurysm is a medical emergency and may cause additional symptoms:
Sudden loss of consciousness can occur.
Seizures may be triggered by a ruptured aneurysm.
Diagnosing a brain aneurysm typically involves a combination of medical tests and imaging studies.
A CT scan of the head can detect the presence of an aneurysm and determine if it has ruptured.
MRI scans provide detailed images of the brain's blood vessels and can reveal the size and location of an aneurysm.
Cerebral angiography is a more invasive test that involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels and taking X-rays to visualize the aneurysm.
Treating a brain aneurysm is essential to prevent rupture and potential life-threatening complications.
Certain medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of complications.
Quitting smoking and managing blood pressure through diet and exercise can help prevent aneurysm growth.
Surgical clipping involves placing a small metal clip at the base of the aneurysm to prevent blood flow.
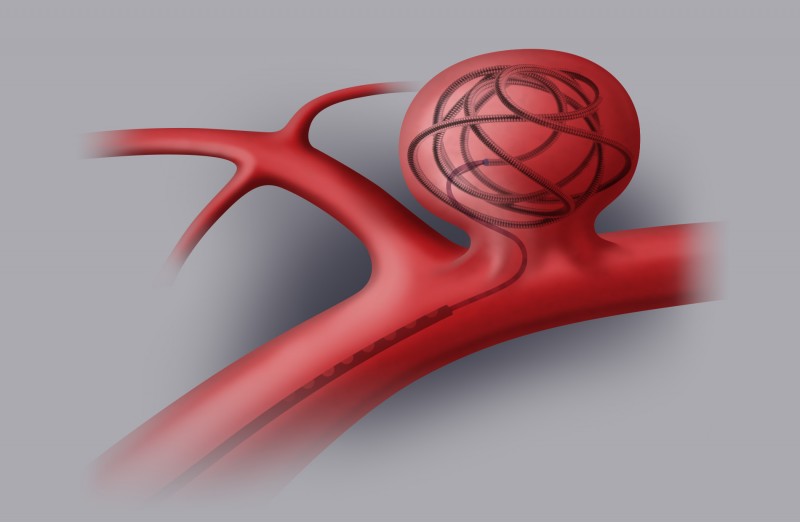
Endovascular coiling is a minimally invasive procedure where a coil is inserted into the aneurysm to block blood flow and promote clotting.
A newer technique involves using a stent-like device to redirect blood flow away from the aneurysm.
Recovering from brain aneurysm treatment can be a lengthy process, and rehabilitation may be necessary.
Patients will be closely monitored in the intensive care unit after surgery.
Rehabilitation may include physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy, depending on the individual's needs.
While not all brain aneurysms can be prevented, certain lifestyle choices can reduce your risk.
Managing hypertension through medication and lifestyle changes is crucial.
Quitting smoking can significantly lower your risk.
Eating a balanced diet and maintaining a healthy weight can also contribute to prevention.
Brain aneurysms are a serious medical condition that requires prompt diagnosis and treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for managing this condition. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms suggestive of a brain aneurysm, seek medical attention immediately.
Exploring Healthier Condiment Choices
7 Ways to Achieve Youthful, Radiant Skin
Understanding Cardiovascular Disease: The Top 5 Modifiable Causes