In this article, we will explore the topic of malaria, a serious and potentially life-threatening disease that affects millions of people worldwide. We will delve into the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention measures associated with this infectious disease. Malaria continues to be a significant health concern, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions. By understanding this disease better, we can work towards its prevention and control.
What is Malaria?: Malaria is a parasitic infection caused by the Plasmodium parasite, which is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected female Anopheles mosquitoes. The disease is prevalent in tropical and subtropical regions, primarily in Africa, Asia, and Latin America. Malaria can be severe and even fatal if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
Causes of Malaria: Malaria is caused by several species of the Plasmodium parasite. When an infected mosquito bites a person, it injects the parasite into their bloodstream. The parasite then travels to the liver, where it matures and multiplies before infecting red blood cells. Mosquitoes become infected by biting an infected person and picking up the parasite, continuing the cycle of transmission.
Types of Malaria: There are five species of the Plasmodium parasite that cause malaria in humans: Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium malariae, Plasmodium ovale, and Plasmodium knowlesi. Among these, P. falciparum is the most dangerous and responsible for the majority of malaria-related deaths.
Signs and Symptoms of Malaria: The symptoms of malaria typically appear 10 to 15 days after the infected mosquito bite. Common symptoms include high fever, chills, headache, sweating, fatigue, body aches, and nausea. In severe cases, malaria can lead to complications such as organ failure, anemia, and cerebral malaria, which affects the brain.
Diagnosis of Malaria: Diagnosing malaria involves laboratory tests that detect the presence of the parasite in the blood. These tests include microscopic examination of blood samples, rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs), and molecular tests like polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial for initiating appropriate treatment.
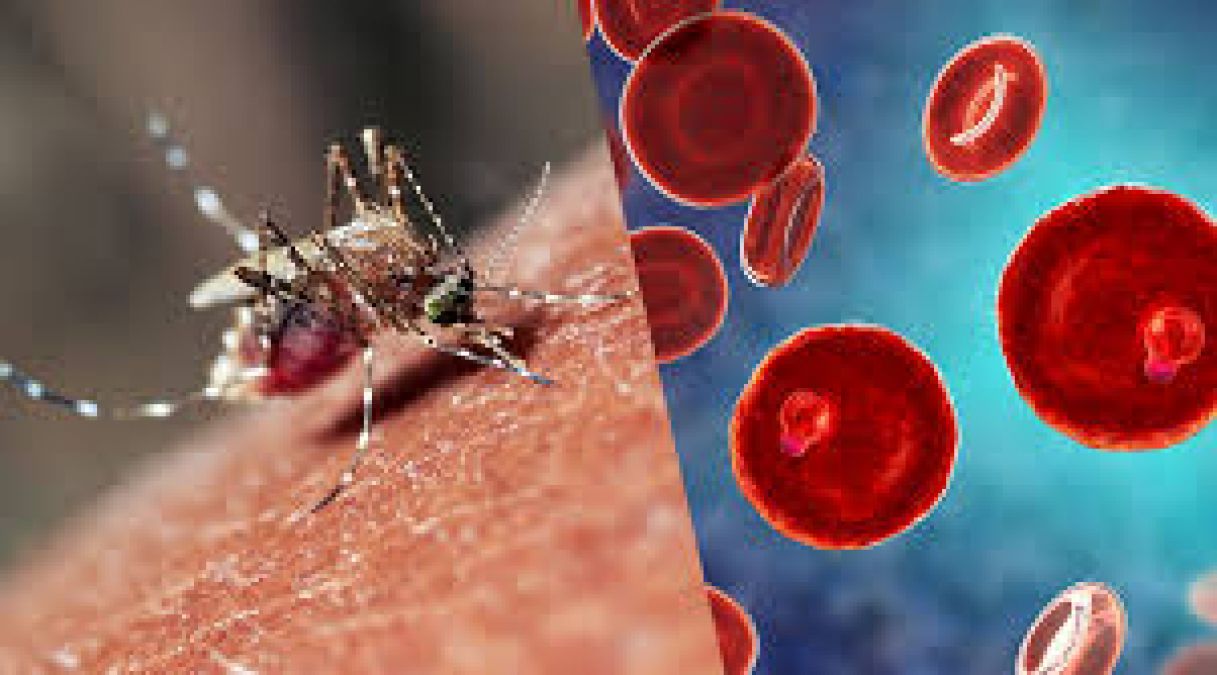
Treatment Options: The treatment for malaria depends on the type of parasite causing the infection and the severity of the disease. Antimalarial medications are commonly used to kill the parasite and alleviate symptoms. Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are the most effective treatment for uncomplicated falciparum malaria. In severe cases, hospitalization and intravenous medications may be necessary.
Prevention and Control Measures: Preventing malaria involves a multi-faceted approach. Key strategies include the use of insecticide-treated bed nets, indoor residual spraying of insecticides, and antimalarial medications for prevention (chemoprophylaxis) in high-risk areas. Mosquito control measures, such as eliminating breeding sites and using insect repellents, also play a crucial role in preventing malaria transmission.

Malaria and Global Impact: Malaria has a significant impact on global health and socio-economic development, particularly in countries with high transmission rates. It affects productivity, hinders economic growth, and poses a burden on healthcare systems. Efforts to combat malaria involve international collaborations, research for new interventions, and strengthening healthcare infrastructure in affected regions.

Conclusion: Malaria remains a pressing global health issue, with millions of people at risk of infection. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention measures associated with malaria is crucial for effective control and eradication of the disease. By implementing comprehensive strategies and raising awareness, we can work towards a malaria-free future.
Exploring the Ultimate Benefits of Eating Pani Puri
Anti-Inflammatory Diet: Include these 5 foods in your diet if you want to reduce swelling and pain