Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) is a serious medical condition that occurs when a blood clot forms in a deep vein, typically in the legs. While DVT can be a silent threat, understanding its warning signs is crucial for early detection and treatment. In this article, we will delve into the key indicators of DVT, helping you recognize the symptoms and seek medical attention promptly.
Deep Vein Thrombosis is a condition that demands awareness, as its symptoms often mimic other less severe issues. In this article, we will guide you through the signs of DVT, aiding in timely recognition and intervention.
Deep Vein Thrombosis occurs when a blood clot forms within a deep vein, most commonly in the legs. If left untreated, these clots can dislodge and travel to the lungs, causing a life-threatening condition known as pulmonary embolism.
Certain factors increase the likelihood of developing DVT. These include a history of blood clotting disorders, prolonged periods of immobility, surgery, obesity, and even genetics.
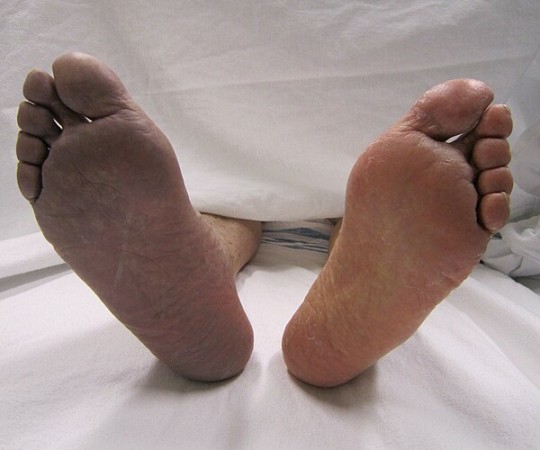
The onset of DVT is often accompanied by pain and swelling in the affected leg. This discomfort might be mistaken for muscle soreness initially, but it persists and worsens over time.
As the condition progresses, the skin over the affected area may become discolored and feel warm to the touch. This is due to impaired blood circulation caused by the clot.
If you find yourself unusually fatigued after minimal physical exertion, it could be a sign of DVT. The clot obstructs blood flow, leading to oxygen deprivation in the muscles.
Prompt medical attention is crucial if you experience persistent pain, swelling, or warmth in your leg. Additionally, if you notice sudden shortness of breath, chest pain, or coughing up blood, it might indicate a clot has traveled to your lungs.
To confirm DVT, doctors may recommend ultrasound scans, blood tests, or venography. These tests help determine the presence, size, and location of the blood clot.
Regular physical activity and staying hydrated enhance blood circulation, reducing the risk of clots. Simple leg exercises can be beneficial during prolonged periods of sitting or standing.
Blood thinners are often prescribed to prevent clot formation. In some cases, a filter might be inserted into the inferior vena cava to prevent clots from reaching the lungs.
Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding smoking, and managing medical conditions like diabetes can significantly lower your risk of DVT.
Being vigilant about the warning signs of Deep Vein Thrombosis can make a life-saving difference. If you suspect DVT based on the symptoms discussed in this article, seek medical help promptly to ensure timely diagnosis and treatment.
Warning Signs of Canker Sores: What to Watch Out For
Nourish Your Body: The Science of Soaked Walnuts
The Hidden Dangers of Tight Bra Straps: Bra Strap Syndrome Explained