In our fast-paced lives, it's not uncommon for individuals to overlook their basic physiological needs, such as eating, drinking, and even urinating, due to hectic schedules and demanding responsibilities. However, what many fail to realize is that neglecting the urge to urinate can have significant repercussions on overall health. In this comprehensive analysis, we delve into the various health implications of prolonged urine retention, shedding light on the physiological mechanisms involved and the potential risks associated with this practice.
Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs):
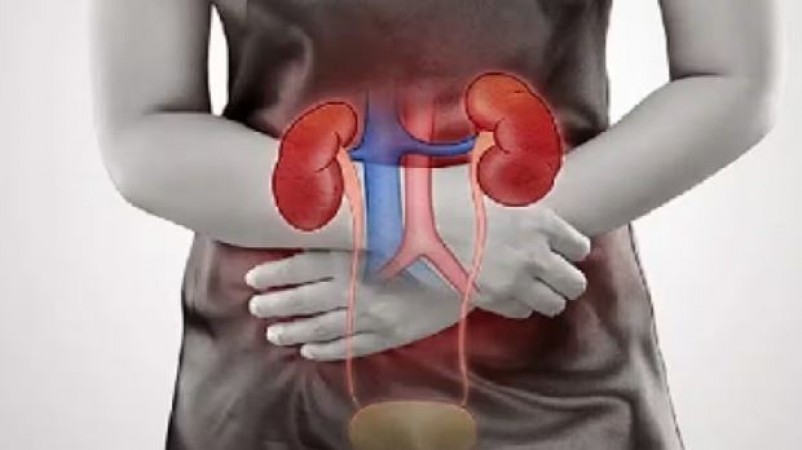
One of the most pressing concerns associated with holding urine for extended periods is the increased risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs). The urinary tract comprises the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, and it serves as the body's drainage system for removing waste and excess fluids. When urine is retained in the bladder for too long, it creates an optimal environment for bacterial growth, leading to UTIs.
The bladder acts as a reservoir for urine, storing it until it is expelled from the body during urination. However, when urine is held for prolonged durations, it provides a breeding ground for bacteria, particularly Escherichia coli (E. coli), which is commonly found in the gastrointestinal tract. As urine stagnates in the bladder, bacterial proliferation occurs, increasing the risk of infection.
Moreover, the pressure exerted on the bladder walls due to urine retention can compromise its integrity, making it more susceptible to bacterial infiltration. This not only heightens the likelihood of UTIs but also exacerbates the severity of the infection. Symptoms of UTIs include frequent urination, burning sensation during urination, cloudy or foul-smelling urine, and pelvic pain.
Prevention of UTIs primarily involves maintaining proper hydration and ensuring timely urination. By emptying the bladder regularly, individuals can minimize the risk of bacterial overgrowth and subsequent urinary tract infections. Additionally, practicing good hygiene, such as wiping from front to back after urination and maintaining clean genitalia, can help prevent the introduction of bacteria into the urinary tract.
Bladder-related Complications:
In addition to UTIs, prolonged urine retention can lead to various complications affecting the bladder itself. The bladder is a muscular organ responsible for storing and expelling urine, and its proper function is crucial for maintaining urinary continence and overall health.
When urine is held for extended periods, the bladder undergoes distension, wherein it becomes excessively stretched beyond its normal capacity. This distension can result in bladder dysfunction and compromise its ability to contract effectively during urination. As a consequence, individuals may experience urinary hesitancy, incomplete emptying of the bladder, and increased urinary frequency.
Furthermore, chronic bladder distension can lead to structural changes in the bladder wall, including hypertrophy (thickening) and fibrosis (scarring). These alterations not only impair bladder function but also predispose individuals to other bladder-related conditions, such as overactive bladder syndrome and urinary incontinence.
Pelvic Floor Weakness and Urinary Leakage:
Another significant consequence of prolonged urine retention is the weakening of the pelvic floor muscles, which can result in urinary leakage and incontinence. The pelvic floor comprises a network of muscles, ligaments, and connective tissues that support the pelvic organs, including the bladder, uterus, and rectum.
When urine is held for prolonged durations, the pelvic floor muscles are subjected to sustained pressure, leading to muscle fatigue and eventual weakening. As a result, individuals may experience urinary leakage, particularly during activities that increase intra-abdominal pressure, such as coughing, sneezing, or lifting heavy objects.
Moreover, chronic pelvic floor weakness can exacerbate existing bladder issues and contribute to the development of pelvic organ prolapse, wherein the pelvic organs descend into the vaginal canal due to inadequate support. This can further exacerbate urinary symptoms and significantly impact quality of life.
To mitigate the risk of pelvic floor weakness and urinary leakage, it is essential to maintain pelvic floor health through regular exercise and proper bladder habits. Pelvic floor exercises, also known as Kegel exercises, can help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles and improve urinary control. Additionally, avoiding prolonged urine retention and practicing timely urination can alleviate pressure on the pelvic floor and reduce the risk of muscle weakening.
Disruption of Urinary Signals:
Prolonged urine retention can disrupt the body's natural signals for urination, leading to confusion and misinterpretation of urinary cues. Normally, the bladder sends signals to the brain when it reaches a certain level of fullness, prompting the urge to urinate. However, when urine is held for extended periods, these signals may become distorted or suppressed, making it difficult for individuals to recognize the need to urinate.
As a result, individuals may ignore or misinterpret the body's signals for urination, leading to delayed or inadequate response. This can further perpetuate the cycle of urine retention, as individuals may continue to hold urine despite experiencing discomfort or urgency.
Moreover, habitual urine retention can desensitize the bladder's sensory receptors, making it less responsive to urinary cues over time. This can exacerbate bladder dysfunction and increase the risk of urinary retention, wherein the bladder is unable to empty fully during urination.
To restore normal bladder function and urinary sensation, it is essential to retrain the bladder and establish healthy voiding habits. This involves listening to the body's signals for urination and responding promptly to alleviate bladder distension and discomfort. Additionally, practicing relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and mindfulness, can help reduce anxiety and improve bladder control.
Impact on Kidney Health:
Beyond the bladder, prolonged urine retention can also affect kidney health and function. The kidneys play a crucial role in filtering waste products and excess fluids from the bloodstream, producing urine that is eventually excreted from the body. However, when urine is held for prolonged durations, it can exert pressure on the kidneys, compromising their ability to function effectively.
The kidneys rely on a delicate balance of fluid and electrolytes to maintain optimal blood pressure and filtration rates. Prolonged urine retention disrupts this balance, leading to fluid retention, electrolyte imbalances, and impaired kidney function. Moreover, the increased pressure within the urinary tract can obstruct urinary flow and increase the risk of kidney stones and urinary obstruction.
Furthermore, chronic urine retention can elevate levels of urea and creatinine in the bloodstream, which are waste products normally excreted through urine. Elevated levels of these substances can indicate impaired kidney function and may necessitate further evaluation and management.
To safeguard kidney health, it is essential to maintain proper hydration and ensure regular urination to prevent urine stagnation and pressure buildup within the urinary tract. Additionally, adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support kidney function and reduce the risk of urinary complications.
The health risks of holding urine extend beyond mere inconvenience and discomfort. From urinary tract infections to kidney damage and urinary leakage, delaying urination can have profound consequences on health. Understanding the mechanisms underlying these risks highlights the importance of prioritizing regular bathroom breaks and listening to the body's signals for urination. By adopting proactive measures to maintain optimal urinary health, individuals can mitigate the potential risks associated with holding urine and promote overall well-being.
Bangkok Urges Work from Home as Pollution Peaks, It's Among Top 10 Most Polluted Cities
How to Enhance Your Sleep with Super Fruits: Try These Nutrient-Packed Foods for a Restful Night
World Hippo Day 2024: Understanding History and Significance of this Celebration