Cushing's disease, a rare but serious medical condition, can affect anyone. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore the warning signs, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for Cushing's disease. Let's dive into this important topic step by step.
Cushing's disease, also known as hypercortisolism, occurs when your body produces an excessive amount of the hormone cortisol. This can result from various factors, including tumors and long-term use of corticosteroid medications.
Cortisol is often referred to as the "stress hormone." It plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, such as metabolism, immune response, and blood pressure.
Cushing's disease can manifest through a range of symptoms. It's essential to be aware of these signs, as early detection can lead to better treatment outcomes.
Unexplained and rapid weight gain, especially in the abdominal area, is a common symptom of Cushing's disease.
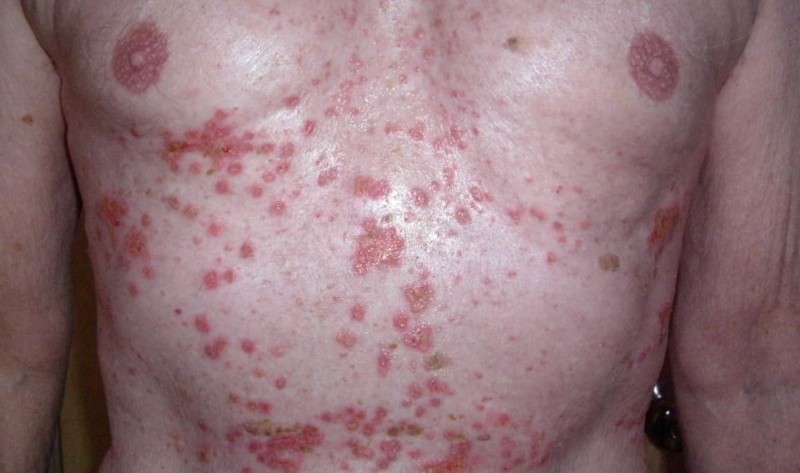
Look out for skin changes such as thinning, easy bruising, and the development of purple stretch marks (striae).
Persistent fatigue and weakness can be indicative of a cortisol imbalance.
Hypertension (high blood pressure) is a potential consequence of excessive cortisol production.
Mood swings, irritability, and anxiety are emotional symptoms associated with Cushing's disease.
Muscle weakness, particularly in the upper arms and thighs, can occur.
For women, menstrual irregularities may be a sign to watch for.
Excessive thirst and urination can be indicators of the disease.
If you suspect you or someone you know may have Cushing's disease, it's crucial to seek medical attention for proper diagnosis.
A thorough physical examination can reveal telltale signs like striae, buffalo hump (fat accumulation on the upper back), and thinning of the skin.
Blood tests can measure cortisol levels, which are typically elevated in Cushing's disease.
A 24-hour urine test helps assess the amount of cortisol excreted in your urine.
Imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans, can identify tumors or abnormalities in the pituitary or adrenal glands.
Once diagnosed, Cushing's disease can be managed with various treatment approaches.
Medications may be prescribed to reduce cortisol production or block its effects.
In some cases, surgical removal of tumors causing the disease may be necessary.
Radiation therapy is an option if surgery is not possible or effective.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet and regular exercise can complement medical treatments.
Cushing's disease is a lifelong condition, but with proper management, many people can lead fulfilling lives.
Scheduled follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor your condition and adjust treatments as needed.
Building a support network with friends and family can provide emotional assistance during your journey.
Understanding your condition is empowering. Educate yourself about Cushing's disease to make informed decisions.
Don't hesitate to seek mental health support to cope with the emotional challenges that may arise.
Cushing's disease is a complex condition that requires careful monitoring and management. By recognizing the warning signs and seeking timely medical attention, individuals can improve their quality of life. Remember that you're not alone, and with the right support and treatment, you can navigate this journey successfully.
The most common medication errors to avoid
Immediate Relief from Acidity and Gas: A Natural Approach
Use of period-delaying medication? Learn how these pills function and what they do