Alopecia areata is a common autoimmune disorder that causes hair loss on the scalp and other parts of the body. It can be distressing and challenging to manage, but with the right knowledge and approach, individuals can effectively cope with this condition. This article will guide you through the recognition and management of alopecia areata, providing valuable insights into the causes, symptoms, treatments, and coping strategies.
What is Alopecia Areata?
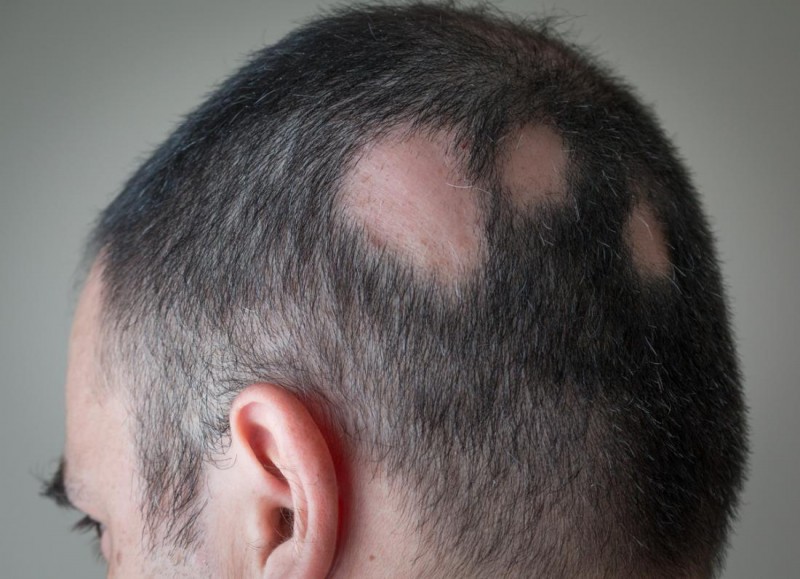
Alopecia areata is a type of hair loss that occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, leading to their inflammation and subsequent hair loss. This condition can affect people of all ages, genders, and ethnic backgrounds. It often starts with small, round patches of hair loss on the scalp, which may spread to other areas over time.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Patchy Hair Loss: The most common symptom of alopecia areata is the appearance of round or oval patches of hair loss on the scalp, beard area, or eyebrows.
Exclamation Mark Hairs: Along the edges of the affected areas, short, broken hairs that resemble exclamation marks may be visible.
Nail Abnormalities: Some individuals with alopecia areata may experience pitting, ridges, or white spots on their fingernails and toenails.
Regrowth and Relapse: Hair regrowth may occur in some cases, but relapses are possible, and the condition may become chronic.
Causes and Triggers
The exact cause of alopecia areata remains unknown, but it is believed to be an autoimmune disease. Genetic factors also play a role, as it can run in families. Certain triggers may activate the condition or worsen existing symptoms:
Stress: Emotional or physical stress can be a triggering factor.
Illness or Infection: Viral or bacterial infections can contribute to hair loss.
Medications: Some medications may lead to temporary hair loss.
Hormonal Changes: Hormonal imbalances can be linked to alopecia areata.
Diagnosing Alopecia Areata
If you notice signs of hair loss or unusual patterns, it's essential to consult a dermatologist or healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. The doctor will examine your scalp and may perform a scalp biopsy or blood tests to rule out other potential causes of hair loss.
Treatment Options
Topical Treatments: Corticosteroid creams or ointments applied to the affected areas can help reduce inflammation and stimulate hair regrowth.
Intralesional Injections: Injections of corticosteroids directly into the bald patches may promote hair growth.
Oral Medications: In some cases, oral corticosteroids or immunosuppressants might be prescribed.
Light Therapy: Light treatments such as phototherapy can aid in hair regrowth.
Minoxidil: Over-the-counter minoxidil solution can be effective for some individuals.
Coping with Alopecia Areata
Support Groups: Joining support groups or connecting with others who have alopecia areata can be empowering and helpful.
Hairstyling: Experiment with different hairstyles or head coverings to boost confidence.
Cosmetics: Some makeup products can camouflage hair loss areas.
Avoiding Triggers: Identify and manage stress and other triggering factors.
Alopecia areata can be a challenging condition to deal with, but with the right information and support, individuals can effectively manage it and regain their confidence. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking early diagnosis, and exploring various treatment options are crucial steps in addressing this condition. Remember, you are not alone, and there are resources available to help you on this journey.
Noise Launches Color Fit Thrive Smartwatch: See Features
Foxconn Commits $500-Mn Investment to Set up 2 Component Factories in India
Google Assistant Set for AI Transformation with LLM Technology, Internal Email Reveals