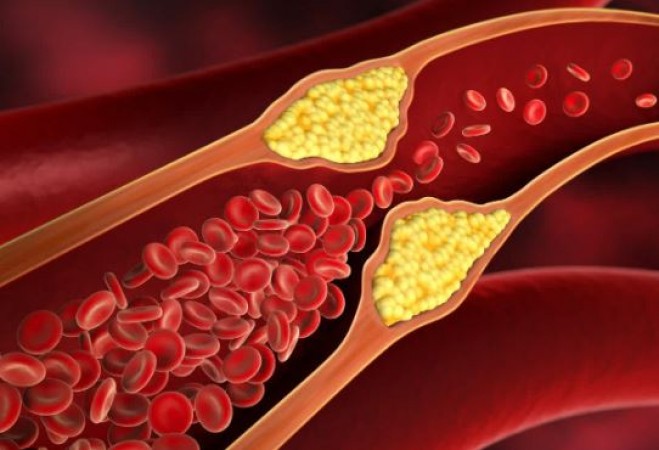
In today's era, the prevalence of high cholesterol among young individuals is rapidly increasing. Cholesterol, a waxy substance found in all cells of the body, plays a crucial role in various physiological functions. While the liver produces cholesterol, certain foods such as meat and dairy products also contribute to its presence in the body. Adequate cholesterol is essential for proper bodily functions, but an excess can lead to the accumulation of cholesterol in the blood vessels, posing a risk of cardiovascular diseases.
Understanding Good and Bad Cholesterol:
Chia Seeds: A Nutrient-Rich Powerhouse
Chia seeds have gained immense popularity in recent years due to their exceptional nutritional profile. These tiny seeds are packed with essential nutrients, making them a valuable addition to a heart-healthy diet.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Chia seeds are an abundant source of Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). Omega-3 fatty acids play a crucial role in cardiovascular health by reducing inflammation, improving blood vessel function, and lowering levels of triglycerides, a type of fat in the blood.
Soluble Fiber Content:
One of the standout features of chia seeds is their high soluble fiber content. Soluble fiber forms a gel-like substance when mixed with liquids, slowing down the digestion and absorption of food. In the context of cholesterol management, soluble fiber binds to cholesterol particles, preventing their absorption into the bloodstream and facilitating their elimination from the body.
Antioxidant Properties:
Chia seeds also boast potent antioxidant properties. Antioxidants neutralize free radicals in the body, which can contribute to oxidative stress and inflammation. By reducing oxidative stress, chia seeds indirectly support heart health and contribute to the overall well-being of the individual.
Weight Management:
Beyond cholesterol control, chia seeds have gained popularity for their role in weight management. The combination of high fiber content and the ability to absorb water contributes to a feeling of fullness, potentially reducing overall calorie intake and aiding in weight loss or weight maintenance.
Practical Incorporation:
Chia seeds are versatile and easy to incorporate into the diet. They can be added to smoothies, yogurt, oatmeal, or used as an egg substitute in baking. This versatility makes it convenient for individuals to enjoy the health benefits of chia seeds regularly.
Oats: The Heart-Healthy Breakfast Staple
Oats have long been recognized as a nutritious and heart-friendly food. They are a staple in many breakfast dishes and offer a range of health benefits, particularly in the context of cholesterol management.
Beta-Glucans and Soluble Fiber:
The primary cholesterol-lowering component in oats is beta-glucans, a type of soluble fiber. Beta-glucans form a gel-like substance in the digestive tract, which binds to cholesterol and helps eliminate it from the body. Regular consumption of beta-glucans has been associated with a reduction in LDL cholesterol levels.
Antioxidant Properties:
Oats also contain antioxidants, including avenanthramides. These antioxidants have anti-inflammatory properties and contribute to overall cardiovascular health. They help protect the delicate balance of cholesterol levels and reduce the risk of oxidative damage to blood vessels.
Blood Sugar Regulation:
In addition to cholesterol benefits, oats contribute to the regulation of blood sugar levels. The soluble fiber in oats slows down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream. This can be particularly beneficial for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
Versatile Culinary Uses:
Oats are incredibly versatile and can be enjoyed in various forms, including oatmeal, granola, and oat flour in baking. This versatility makes it easy for individuals to incorporate oats into their daily meals and snacks, promoting heart health without compromising on taste.
Dry Fruits: Nutrient-Rich Snacking for Heart Health
Dry fruits, including almonds, walnuts, and other nuts, are nutrient-dense snacks that offer a myriad of health benefits, especially concerning heart health and cholesterol management.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Walnuts:
Walnuts stand out among dry fruits due to their high content of Omega-3 fatty acids, primarily alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). These essential fatty acids have anti-inflammatory effects and contribute to the maintenance of a healthy cardiovascular system. Regular consumption of walnuts has been linked to a reduced risk of heart disease.
Monounsaturated Fats in Almonds:
Almonds are rich in monounsaturated fats, which are heart-healthy fats associated with improved cholesterol levels. These fats, along with vitamin E and antioxidants found in almonds, contribute to the overall cardiovascular benefits of this nut.
Fiber-Rich Content:
All dry fruits, including cashews, almonds, and walnuts, contain significant amounts of dietary fiber. Fiber plays a vital role in cholesterol management by binding to cholesterol molecules and aiding in their elimination from the body. Additionally, the fiber content contributes to a feeling of fullness, potentially preventing overeating and supporting weight management.
Micronutrient Powerhouse:
Dry fruits are not only a source of healthy fats and fiber but also provide essential vitamins and minerals. These include vitamin E, magnesium, and potassium, which play crucial roles in maintaining heart health, regulating blood pressure, and supporting overall well-being.
Portion Control and Moderation:
While dry fruits offer numerous health benefits, it's essential to consume them in moderation due to their calorie density. Incorporating a handful of mixed nuts or a small portion of dry fruits into the daily diet can provide the desired health benefits without excessive calorie intake.
Incorporating chia seeds, oats, and dry fruits into one's diet can be a proactive and delicious approach to managing cholesterol levels and promoting heart health. These foods offer a combination of heart-protective nutrients, including Omega-3 fatty acids, soluble fiber, antioxidants, and essential vitamins and minerals.
It's crucial to emphasize that while specific foods can contribute to cholesterol management, an overall healthy lifestyle plays a pivotal role. This includes regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, avoiding excessive consumption of processed foods and trans fats, and managing stress levels.
By making informed dietary choices and adopting a holistic approach to health, individuals can take charge of their well-being and reduce the risk of cardiovascular issues. Regular consultation with healthcare professionals and nutritionists can provide personalized guidance based on individual health conditions and goals. Ultimately, a combination of mindful eating, regular exercise, and overall well-being practices forms the foundation for a heart-healthy life.
Maharashtra Agriculture Minister Dhananjay Munde Tests Positive for COVID-19
What will happen if you eat idli and sambar continuously for a month? Know from health expert