Vitamin D, often dubbed the "sunshine vitamin," is a vital nutrient that the body produces when exposed to sunlight. It plays a multifaceted role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Functions of Vitamin D
1. Calcium Absorption
One of the primary functions of vitamin D is facilitating the absorption of calcium in the gut. Calcium is essential for maintaining strong bones and teeth, making vitamin D crucial for skeletal health.
2. Muscle Function
Beyond its role in bone health, vitamin D also supports muscle function and strength. Adequate levels of this vitamin are necessary to prevent muscle weakness and maintain optimal performance.
3. Immune System Support
Vitamin D contributes to the proper functioning of the immune system, helping the body defend against infections and diseases. It plays a role in regulating immune responses and reducing inflammation.
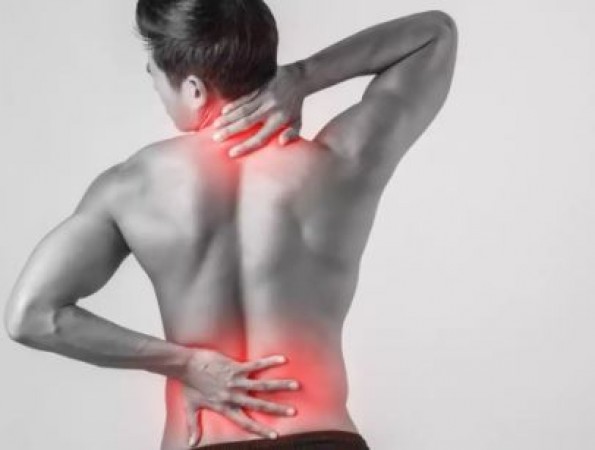
Understanding Back Pain
Defining Back Pain
Back pain is a prevalent health issue characterized by discomfort or pain felt anywhere along the spine, from the neck down to the lower back. It can range from mild and intermittent to severe and chronic, significantly impacting an individual's quality of life.
1. Causes of Back Pain
- Poor Posture: Incorrect posture while sitting, standing, or lifting heavy objects can strain the muscles and lead to back pain.
- Muscle Strain: Overuse, sudden movements, or lifting heavy objects improperly can cause muscle strains, resulting in pain and discomfort in the back.
- Injury or Trauma: Accidents, falls, or sports injuries can damage the muscles, ligaments, or discs in the back, leading to acute or chronic pain.
The Link Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Back Pain
1. Muscle Weakness
- Impact of Vitamin D Deficiency: Insufficient levels of vitamin D can lead to muscle weakness and fatigue. Weak muscles are more prone to strain and injury, contributing to back pain.
- Clinical Studies: Research has indicated that individuals with low vitamin D levels may experience more significant muscle weakness and are at a higher risk of developing musculoskeletal conditions, including back pain.
2. Bone Health
- Importance of Vitamin D: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in maintaining bone health by aiding in the absorption of calcium. Without adequate vitamin D, bones can become weak and brittle, increasing the risk of fractures and osteoporosis.
- Association with Back Pain: Weak bones due to vitamin D deficiency may manifest as back pain, especially in the lumbar spine area. Chronic low back pain can be a symptom of underlying bone-related issues exacerbated by inadequate vitamin D levels.
3. Inflammation
- Inflammatory Response: Vitamin D deficiency has been linked to increased inflammation in the body, which can contribute to chronic pain conditions, including back pain.
- Role in Pain Perception: Inflammation can sensitize nerve endings and heighten pain perception, exacerbating discomfort in individuals with back pain and concurrent vitamin D deficiency.
Recognizing Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
1. Fatigue
- Feeling Exhausted: Persistent fatigue, even after getting adequate rest, may indicate low vitamin D levels.
- Impact on Daily Functioning: Fatigue can impair daily activities and reduce quality of life, affecting work performance and overall well-being.
2. Muscle Pain
- Generalized Aches and Pains: Muscle aches and pains, particularly in the back and legs, are common symptoms of vitamin D deficiency.
- Difficulty Moving: Individuals may experience discomfort or stiffness, making movements challenging and uncomfortable.
3. Bone Pain
- Localized Discomfort: Bone pain, especially in areas like the back, hips, and legs, can be indicative of vitamin D deficiency.
- Increased Vulnerability: Weakened bones are more susceptible to pain and discomfort, particularly under stress or strain.
4. Mood Changes
- Emotional Instability: Vitamin D deficiency has been associated with mood disorders such as depression, anxiety, and irritability.
- Impact on Mental Health: Addressing vitamin D deficiency may alleviate mood symptoms and improve overall psychological well-being.
Prevention and Treatment of Vitamin D Deficiency
1. Sun Exposure
- Optimizing Sunlight Exposure: Spending time outdoors in sunlight, particularly during midday when UVB rays are most intense, can stimulate vitamin D production in the skin.
- Balancing Sun Safety: While sunlight is a natural source of vitamin D, it's essential to practice sun safety to minimize the risk of skin damage and sunburn.
2. Dietary Sources
- Incorporating Vitamin D-Rich Foods: Including foods high in vitamin D in the diet can help maintain adequate levels. Sources include fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, tuna), fortified dairy products (milk, yogurt, cheese), egg yolks, and fortified cereals.
- Supplementation: In cases where dietary intake and sun exposure are insufficient, vitamin D supplements may be recommended to bridge the gap and ensure optimal levels.
Vitamin D deficiency is a common yet often overlooked issue that can have significant implications for musculoskeletal health, including back pain. Understanding the interplay between vitamin D levels and back pain is crucial for effective prevention and management strategies. By promoting adequate sun exposure, incorporating vitamin D-rich foods into the diet, and considering supplementation when necessary, individuals can optimize their vitamin D status and potentially alleviate symptoms of back pain.
Tata-Owned Air India Cuts 180 Jobs, Cites Business Streamlining
Top 10 Wholesale Business Ideas
You can register the location of your home on Google Maps, know the process