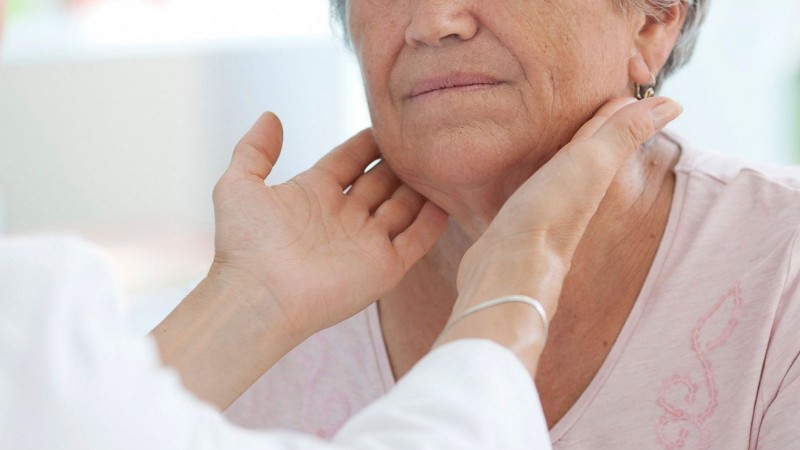
Thyroid disorders are prevalent, affecting millions worldwide. If you're experiencing fatigue, sensitivity to cold, or unexplained weight gain, your thyroid gland might be the culprit. Let's delve into this intricate gland's role in your body and how its dysfunction can manifest in various symptoms.
What is the Thyroid Gland? The thyroid gland, located in the neck, is a butterfly-shaped organ responsible for producing hormones crucial for regulating metabolism, energy levels, and body temperature. Despite its small size, the thyroid plays a significant role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Thyroid Hormones Thyroid hormones include thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are synthesized from iodine and tyrosine and are essential for the proper functioning of almost every cell in the body. They play a vital role in regulating metabolism, growth, and development, as well as maintaining the function of the cardiovascular, nervous, and reproductive systems.
Role of Thyroid-Stimulating Hormone (TSH) The production of thyroid hormones is regulated by a feedback loop involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and thyroid gland. The pituitary gland releases thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which stimulates the thyroid gland to produce and release T4 and T3. Elevated TSH levels indicate that the thyroid gland is not producing enough hormones, a condition known as hypothyroidism. Conversely, low TSH levels may indicate hyperthyroidism, where the thyroid gland produces an excess of hormones.
Hypothyroidism Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones to meet the body's needs. This condition affects millions of people worldwide and is more common in women and older adults. Symptoms of hypothyroidism can vary widely but often include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin, hair loss, constipation, and depression. In severe cases, untreated hypothyroidism can lead to complications such as heart disease, infertility, and mental health disorders.
Causes of Hypothyroidism The most common cause of hypothyroidism is autoimmune thyroiditis, also known as Hashimoto's disease, where the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland. Other causes include iodine deficiency, certain medications (such as lithium and amiodarone), radiation therapy, pituitary gland dysfunction, and congenital thyroid abnormalities.
Hyperthyroidism Hyperthyroidism is the opposite of hypothyroidism and occurs when the thyroid gland produces an excess of thyroid hormones. This condition can lead to symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, heat intolerance, sweating, tremors, anxiety, and irritability. If left untreated, hyperthyroidism can cause serious complications such as heart palpitations, osteoporosis, and thyroid storm, a life-threatening condition characterized by extreme elevations in heart rate, body temperature, and blood pressure.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism The most common cause of hyperthyroidism is Graves' disease, an autoimmune disorder where antibodies stimulate the thyroid gland to produce excess hormones. Other causes include thyroid nodules or adenomas, thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid gland), excessive iodine intake, and certain medications (such as thyroid hormone replacement therapy and amiodarone).
Thyroid Function Tests Diagnosis of thyroid disorders typically involves a combination of blood tests and imaging studies. Thyroid function tests measure levels of thyroid hormones (TSH, T4, and T3) in the blood. Elevated TSH levels with low T4 indicate hypothyroidism, while low TSH levels with high T4 suggest hyperthyroidism. Additional tests, such as thyroid antibody tests and thyroid ultrasound, may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and identify underlying causes of thyroid dysfunction.
Imaging Studies Ultrasound imaging of the thyroid gland can detect abnormalities such as thyroid nodules, enlargement (goiter), or inflammation (thyroiditis). Other imaging tests, such as thyroid scans and radioactive iodine uptake tests, may be used to evaluate thyroid function and detect abnormalities not visible on ultrasound.
Hypothyroidism Treatment Treatment for hypothyroidism typically involves lifelong thyroid hormone replacement therapy to restore hormone levels and alleviate symptoms. The most commonly prescribed medication is levothyroxine, a synthetic form of T4 hormone. Regular monitoring of thyroid function and adjustment of medication dosage may be necessary to maintain optimal hormone levels and prevent complications.
Hyperthyroidism Treatment Treatment options for hyperthyroidism depend on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Antithyroid medications, such as methimazole and propylthiouracil, are often used to inhibit the production of thyroid hormones. Radioactive iodine therapy may be recommended to destroy or shrink the thyroid gland and reduce hormone levels. In some cases, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland (thyroidectomy) may be necessary, especially if other treatments are ineffective or contraindicated.
Healthy Diet Maintaining a healthy diet is essential for supporting thyroid function and overall health. Foods rich in iodine, such as seafood, dairy products, and iodized salt, can help prevent iodine deficiency and support thyroid hormone production. However, excessive iodine intake should be avoided, especially in individuals with autoimmune thyroid disease, as it may exacerbate thyroid inflammation and dysfunction.
Stress Management Chronic stress can negatively impact thyroid function and exacerbate symptoms of thyroid disorders. Incorporating stress-reducing activities such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and relaxation techniques can help improve overall well-being and alleviate symptoms associated with thyroid dysfunction. Thyroid disorders are common and can have a significant impact on overall health and quality of life. If you're experiencing symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, or changes in mood or energy levels, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional for evaluation and diagnosis. With proper diagnosis and management, thyroid disorders can be effectively treated, allowing individuals to lead healthy and fulfilling lives.
Do dark circles indicate poor health? Is this a health problem?
You also have the habit of applying mascara again and again! These losses can occur
Do these yoga asanas after waking up in the morning, you will remain energetic throughout the day