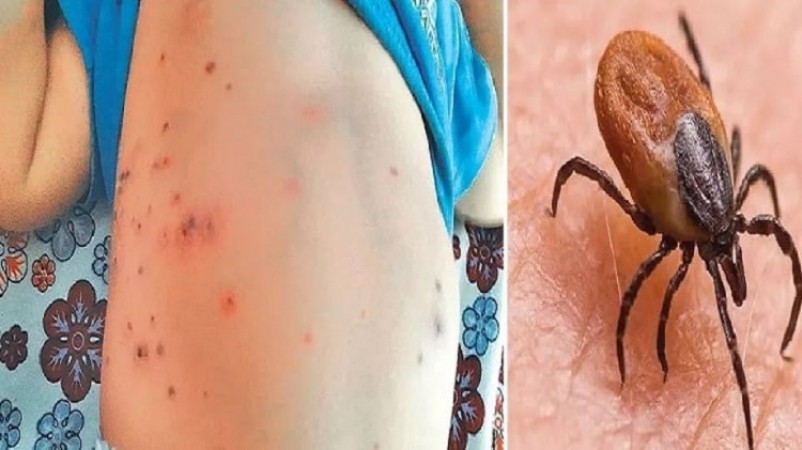
New Delhi: Amidst India's annual battle with various viral outbreaks, regions like Odisha and Shimla have been grappling with the resurgence of scrub typhus cases. Recent reports have revealed a grim situation, with Odisha confirming five fatalities attributed to scrub typhus, while Himachal Pradesh's Shimla has recorded nine casualties. Sadhu Charan Das, the chief district medical and public health officer for Bargarh district in Odisha, discloses that two of the five tragic cases emerged from the Sohela block, with the remaining cases originating in the Attabira, Bheden, and Barpali blocks, respectively.
Understanding Scrub Typhus: Scrub typhus, also known as bush typhus, is instigated by the bacterium Orientia tsutsugamushi. This infection is contracted through the bites of infected chiggers, which are larval mites.
Top 5 Key Facts About Scrub Typhus: Clinical Presentation: Scrub typhus primarily manifests with symptoms such as fever, headache, body aches, and sporadic rashes. Additionally, it can impact mental health, with severe cases experiencing mental changes ranging from confusion to coma. Patients have also reported gastrointestinal symptoms, as well as enlargement of the liver and spleen, and even meningitis during the course of the infection.
Duration of Illness: According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), scrub typhus fever can persist for two to three weeks. Delayed treatment can exacerbate the condition, and up to 5% of individuals infected with flea-transmitted typhus may succumb to it.
High-Risk Groups: People involved in gardening and outdoor activities face a heightened risk of bacterial infection.
Diagnostic Methods: Scrub typhus can be diagnosed through various tests. Physicians may recommend blood tests to detect the infection. The National Library of Medicine (NIH) has outlined several diagnostic tests, including enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), immunofluorescence assay (IFA), immunochromatographic test (ICT), Weil–Felix, polymerase chain reaction (PCR), and loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP).
Preventative Measures: Experts stress the importance of preventive measures against bacterial and viral infections. Practices such as rodent control, maintaining cleanliness, and adhering to hygiene standards can help prevent infection. Additional precautions include using mite repellent on exposed skin, handling pets with care, and regularly cleaning the environment, including clearing shrubs and low vegetation.
Nipah Outbreak in Kerala: Vital Health Department Recommendations
NIPAH: NIA Teams Arrive in Kozhikode, Sets up Mobile Lab for Virus Testing