Angioplasty, also known as percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA), is a common medical procedure aimed at treating coronary artery disease (CAD) by restoring blood flow to the heart. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of angioplasty, exploring its procedure, indications, associated risks, and the financial considerations involved.
Understanding Angioplasty:
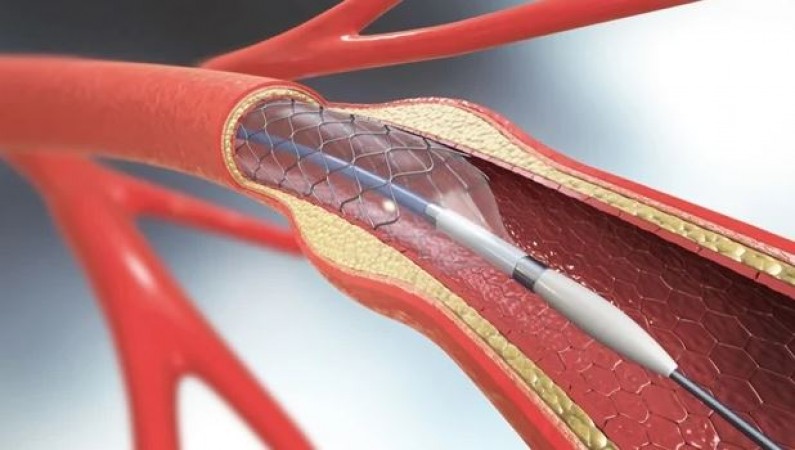
Angioplasty is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to widen narrowed or blocked coronary arteries, which are responsible for supplying blood to the heart muscle. This blockage is typically caused by the buildup of plaque, a combination of cholesterol, fat, and other substances. During angioplasty, a catheter with a deflated balloon attached to its tip is inserted into the blocked artery. Once positioned, the balloon is inflated, compressing the plaque against the artery walls and widening the arterial lumen, thus restoring blood flow.
Indications for Angioplasty:
Atherosclerosis: Atherosclerosis, characterized by the hardening and narrowing of arteries due to plaque buildup, is a primary indication for angioplasty. Individuals experiencing symptoms such as chest pain (angina) or shortness of breath may require this procedure to alleviate their symptoms and improve blood flow to the heart.
Heart Attack Risk Reduction: Angioplasty is often recommended for individuals at high risk of heart attacks, especially those with a history of coronary artery disease or other cardiac conditions. By opening blocked arteries, angioplasty helps reduce the risk of heart attacks and associated complications.
Diabetes: Diabetic patients with coronary artery disease may benefit from angioplasty to restore normal blood flow to the heart and prevent further cardiovascular complications.
Coronary Artery Blockages: Blockages in the coronary arteries, whether partial or complete, can impede blood flow to the heart, leading to chest pain or heart attacks. Angioplasty is employed to remove these blockages and restore optimal blood circulation.
Angina Relief: Angina, a symptom of coronary artery disease characterized by chest pain or discomfort, can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Angioplasty aims to alleviate angina symptoms by improving blood flow to the heart muscles.
Risks Associated with Angioplasty:
Despite being a relatively safe procedure, angioplasty carries certain risks, particularly in patients with specific medical conditions or anatomical complexities. These risks include:
Advanced Age: Older patients may have weaker blood vessels and a higher likelihood of complications during angioplasty.
Multiple Comorbidities: Individuals with multiple medical conditions, such as diabetes, kidney disease, or lung problems, may experience heightened risks during angioplasty.
Diabetes: Diabetic patients are at an increased risk of complications, including delayed wound healing and infection, following angioplasty.
Kidney Damage: Angioplasty can potentially worsen kidney function, especially in patients with pre-existing kidney disease or impaired renal function.
Fluid in the Lungs: Patients with fluid accumulation in the lungs (pulmonary edema) may experience exacerbation of symptoms following angioplasty.
Weak Heart: Patients with compromised heart function or heart failure may be at a higher risk of complications during and after angioplasty.
Low Blood Pressure: Individuals with low blood pressure may experience further drops in blood pressure during angioplasty, potentially leading to complications such as dizziness or fainting.
Complex Artery Structure: Anatomical variations or complex arterial blockages may pose challenges during angioplasty, increasing the risk of procedural complications.
Arterial Blockages with Calcification: Calcified arterial plaques can make angioplasty more technically challenging and increase the risk of complications such as vessel injury or dissection.
Cost of Angioplasty:
The cost of angioplasty can vary significantly depending on factors such as the hospital's reputation, geographic location, and the complexity of the procedure. In general, the cost includes expenses related to pre-operative evaluations, the procedure itself, hospitalization, post-operative care, and any associated medications or follow-up visits. Government hospitals may offer angioplasty at subsidized rates, typically ranging from 20,000 to 30,000 INR. In contrast, private hospitals may charge substantially higher fees, with the total cost of angioplasty ranging from 2 to 5 lakhs INR or more, depending on the hospital's facilities and the specific needs of the patient.
Angioplasty is a crucial intervention for individuals with coronary artery disease, offering relief from symptoms, reducing the risk of heart attacks, and improving overall cardiac health. However, it is essential to understand the procedure's indications, associated risks, and financial implications to make informed decisions regarding treatment options. With advancements in medical technology and techniques, angioplasty continues to be a cornerstone in the management of coronary artery disease, providing patients with improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
THESE Morning Drinks to Help Shrink Your Belly, Try Now
You can reduce your weight by drinking the water of this fruit