Yellow fever, a viral disease with a long history, remains a significant health concern in many parts of the world. It's essential to understand what yellow fever is, how it manifests, its causes, and the available treatment options. Let's dive into the details.
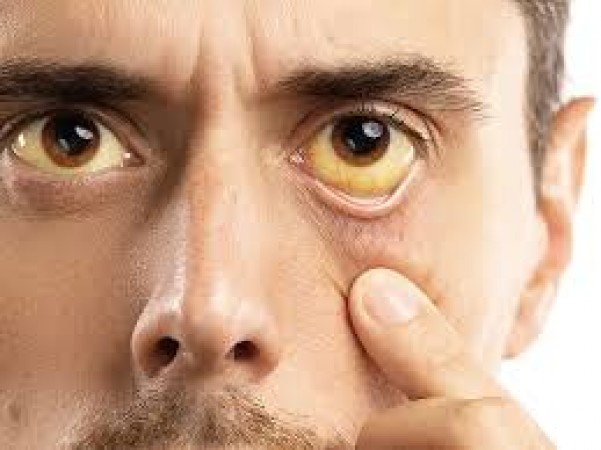
Yellow fever is a viral hemorrhagic disease transmitted by infected mosquitoes. It primarily affects humans and some primates. The disease gets its name from the jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes) that occurs in severe cases.
Yellow fever has plagued humanity for centuries. Outbreaks have been recorded in Africa and the Americas, causing widespread illness and death. The development of a vaccine in the 20th century marked a significant breakthrough in controlling the disease.
The initial symptoms of yellow fever can be quite vague, making early detection challenging. They typically appear 3 to 6 days after being bitten by an infected mosquito.
The first and most obvious symptom is a sudden onset of fever. This is usually high and can come on very quickly.
Alongside the fever, patients often experience chills and intense headaches. These symptoms can be severe and debilitating.
Muscle aches, especially in the back and knees, are common. These pains can be quite severe and often lead to significant discomfort.
In about 15% of cases, the disease progresses to a more severe stage known as the toxic phase. This occurs after a brief remission of symptoms.
One of the hallmark signs of the toxic phase is jaundice, characterized by yellowing of the skin and eyes.
Severe cases can lead to bleeding from the nose, mouth, and eyes. This internal bleeding is a serious complication.
The liver and kidneys can fail, leading to a potentially fatal situation.
The primary cause of yellow fever is the bite of an infected Aedes or Haemagogus mosquito. These mosquitoes thrive in tropical and subtropical regions.
The virus is transmitted between humans and mosquitoes, but it can also spread to non-human primates, creating a cycle of infection.
Environmental conditions, such as warm temperatures and standing water, facilitate the breeding of mosquitoes, thus increasing the risk of yellow fever transmission.
Human activities, including deforestation and urbanization, can increase contact between humans and infected mosquitoes, elevating the risk of outbreaks.
There is no specific antiviral treatment for yellow fever. The mainstay of management is supportive care to alleviate symptoms and support the body's recovery process.
Maintaining hydration is crucial, especially if the patient is experiencing vomiting and diarrhea.
Medications like acetaminophen can help manage pain and reduce fever. Aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) should be avoided due to the risk of bleeding.
Severe cases may require hospitalization for intensive supportive care, including:
IV fluids can help maintain blood pressure and hydration levels.
In cases of significant bleeding, blood transfusions may be necessary.
If the kidneys fail, dialysis might be needed to support kidney function.
The most effective way to prevent yellow fever is through vaccination. The yellow fever vaccine is safe, effective, and provides lifelong immunity for most people.
Controlling the mosquito population is critical in preventing yellow fever.
Removing standing water around homes and communities can help reduce mosquito breeding grounds.
Using insect repellents and wearing long sleeves and pants can reduce the risk of mosquito bites.
Governments and health organizations play a crucial role in controlling yellow fever through vaccination campaigns and public education efforts.
Community awareness and involvement are vital in the fight against yellow fever. Education campaigns can help people understand the risks and preventive measures.
International health organizations, such as the World Health Organization (WHO), work to control yellow fever through global vaccination initiatives and monitoring outbreaks.
Despite advances in vaccination and mosquito control, yellow fever outbreaks still occur. Staying informed about current outbreaks is essential, especially for travelers.
Travelers should check for yellow fever travel advisories and vaccination requirements before visiting endemic areas. Yellow fever, though an ancient disease, continues to pose a threat in many parts of the world. Understanding the symptoms, causes, and treatment methods is crucial in managing and preventing this potentially deadly disease. Vaccination and mosquito control remain the most effective strategies in the fight against yellow fever. By staying informed and taking preventive measures, we can protect ourselves and our communities from this formidable virus.
Carry this type of jewelery with heavy lehenga
Abhiishek Mohta and Smriti Pandey Land Lead Roles in Immigration Agency Advertisement
Peaceful Protests in Mizoram Against Govt's India Border Myanmar Border Decision