Have you ever wondered why certain individuals experience skin loss or shedding? This intriguing phenomenon can be attributed to various factors, shedding light on both natural and medical aspects that influence this occurrence. In this article, we'll delve into the reasons behind why some people lose skin and explore the underlying mechanisms that contribute to this intriguing process.
Understanding the Natural Skin Renewal Process
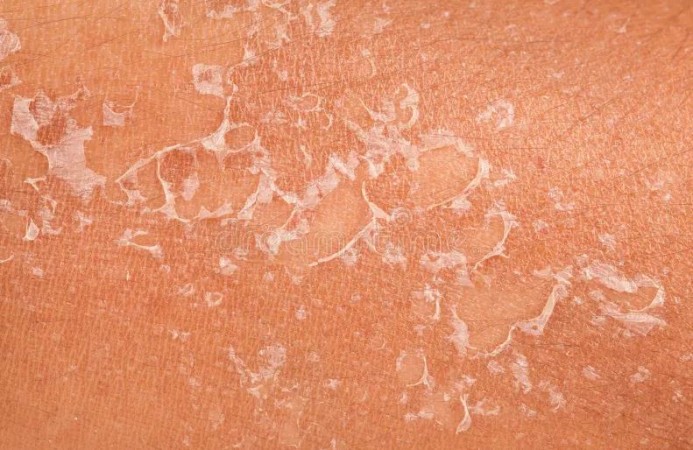
The skin is a remarkable organ with a unique ability to constantly renew itself. This rejuvenation process involves the shedding of old skin cells to make way for new ones. At the cellular level, the epidermis – the outermost layer of skin – is composed of several layers of cells. As newer cells are formed in the lower layers, older ones gradually migrate to the surface. This migration ultimately leads to the shedding of dead skin cells, which is a normal part of the skin's renewal cycle.
Factors That Influence Skin Shedding
- Age and Cell Turnover Rate
- Younger individuals tend to experience more frequent skin shedding due to faster cell turnover.
- As we age, this turnover rate slows down, leading to a buildup of dead skin cells, which can result in a dull complexion.
- Environmental Factors
- Harsh weather conditions, such as extreme cold or dryness, can strip the skin of its natural moisture and cause flaking.
- Overexposure to the sun's UV rays can accelerate the breakdown of collagen and elastin, leading to premature skin shedding.
- Skin Conditions
- Conditions like psoriasis and eczema can disrupt the skin's normal shedding process, causing an overproduction of skin cells that accumulate on the surface.
Medical Reasons for Skin Loss
- Autoimmune Disorders
- Certain autoimmune disorders, such as pemphigus and pemphigoid, cause the immune system to attack skin cells, resulting in blistering and shedding.
- Infections
- Fungal, bacterial, or viral infections can damage the skin's integrity, leading to peeling or shedding as the body fights off the infection.
- Medications and Treatments
- Some medications, like chemotherapy drugs, can affect rapidly dividing cells, including those in the skin, leading to shedding.
- Chemical peels or laser treatments intentionally induce controlled skin shedding as part of the skin rejuvenation process.
Coping Strategies and Prevention
- Hydration: Keeping the skin well-hydrated can prevent excessive dryness and flaking.
- Sun Protection: Regular use of sunscreen helps protect the skin from UV-induced damage and premature shedding.
- Gentle Cleansing: Using mild cleansers and exfoliating gently can help remove dead skin cells without causing irritation.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Consuming a balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants supports overall skin health.
The shedding of skin is a natural process driven by cellular renewal and various external factors. While some individuals might experience more noticeable shedding due to age, environment, or medical conditions, it's essential to understand that the skin's ability to renew itself is a sign of its vitality. By adopting a skincare routine that considers hydration, protection, and a healthy lifestyle, you can support your skin's natural renewal process and maintain its radiant glow.
7 Tips for Enhancing Bone and Joint Health in Your 40s
The Best Ways To Support Your Dog Through Separation Anxiety
Elevate Your Lunch Game: Quick and Easy Sandwich Ideas