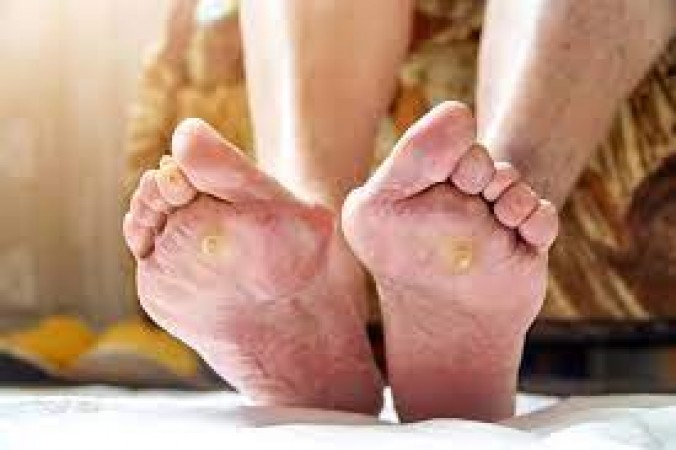
Diabetes, a prevalent metabolic disorder, not only impacts blood sugar levels but also poses challenges in wound healing. Understanding why wounds take longer to heal in diabetic patients and implementing strategies to mitigate this delay is crucial for effective management. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this phenomenon and explore ways to promote timely wound recovery.
Diabetes often leads to vascular complications, hindering the efficient delivery of oxygen and essential nutrients to the wound site. Consequently, this impairs the body's ability to initiate and sustain the healing process.
Diabetic neuropathy, characterized by nerve damage, diminishes sensation in the extremities. Patients may not notice minor injuries, allowing them to progress into serious wounds before seeking treatment.
High blood sugar levels weaken the immune system, making diabetic individuals more susceptible to infections. Infections further impede wound healing, creating a vicious cycle of delayed recovery.
Chronic inflammation, a hallmark of diabetes, disrupts the delicate balance of cytokines and growth factors essential for wound healing. Excessive inflammation can prolong the inflammatory phase, delaying subsequent stages of healing.
Maintaining blood sugar levels within the target range is paramount for promoting wound healing in diabetic patients. Adherence to prescribed medications, dietary modifications, and regular monitoring are indispensable in achieving glycemic stability.
Implementing meticulous wound care practices is essential to prevent infections and facilitate healing. This includes cleaning the wound with mild soap and water, applying appropriate dressings, and regularly monitoring for signs of infection.
For diabetic foot ulcers, offloading pressure from the affected area is imperative to prevent further tissue damage and promote healing. Utilizing specialized footwear or orthotic devices can alleviate pressure and reduce the risk of recurrent ulcers.
Adequate nutrition plays a pivotal role in wound healing. Diabetic patients should consume a balanced diet rich in protein, vitamins, and minerals to provide the body with the necessary building blocks for tissue repair.
Smoking adversely affects circulation and impairs immune function, exacerbating the challenges of wound healing in diabetic individuals. Quitting smoking can significantly improve vascular health and enhance the body's healing capacity.
Close monitoring of wounds and timely intervention are essential components of diabetic wound management. Regular follow-up visits with healthcare providers enable early detection of complications and adjustment of treatment strategies as needed. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of delayed wound healing in diabetic patients empowers healthcare providers and individuals alike to implement proactive measures for optimal wound management. By addressing contributing factors such as impaired circulation, neuropathy, and compromised immune function, and adopting strategies to promote glycemic control, meticulous wound care, and healthy lifestyle habits, diabetic individuals can enhance their prospects for timely wound recovery and prevent the onset of chronic complications.
Volkswagen launches Tigun GT Plus Sport and GT Line, see price and features
This Skoda car got a reduction of Rs 2 lakh, take advantage of the opportunity
Waiting period of Scorpio N and XUV700 reduced, delivery will be available in this number of days