New Delhi [India], Jan 29 (NT): Here are the highlights of the Economic Survey 2017-18 tabled during the commencement of Budget session 2018 by FM Arun Jaitley-
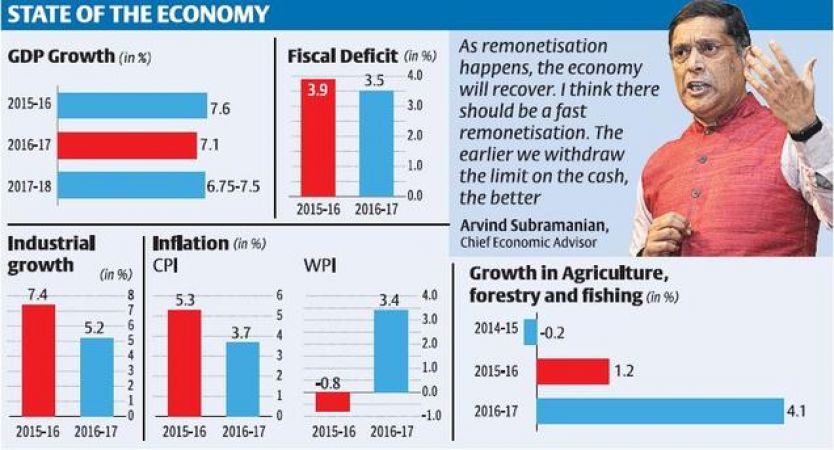
1. India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth for 2018-19 was anticipated at 7 to 7.5 percent. The survey noted that the series of major economic reforms (i.e., note ban and the introduction of GST) which were undertaken over the past year will agree to real GDP growth to reach 6.75 percent this fiscal and will increase to 7.0 to 7.5 percent in 2018-19.
2. There has been a fifty percent rise in the number of indirect tax filers after the introduction of Goods and Services Tax (GST). Many have willingly chosen to be part of GST, especially small enterprises that buy from large enterprises and want to gain themselves of input tax credits. Further, there has been an addition of about 18 lakh in individual income tax filers since November 2016.
3. The inflation numbers presented during 2017-18 averaged at a six-year low of 3.3 percent in 2017-18. The cry off in the inflation was due to major commodity groups except, housing and fuel & light. The survey further noted that the economy witnessed a gradual transition from a period of high and variable inflation to more stable prices in the last four years. Headline inflation measured by the Consumer Price Index (CPI) remained under control for the fourth successive year.
4. The Textile package boosted exports of key man-made ready-made garments by 16 percent. The Rebate of State Levies (ROSL) has increased exports of readymade garments (man-made fibers). ROSL increased export incentives by between 2.8 percent to 3.9 percent.
5. Note ban helped share of financial saving to increase. The ratio of domestic saving to GDP reached 29.2 percent in 2013 to a peak of 38.3 percent in 2007, before falling back to 29 percent in 2016. Further, the cumulative fall over 2007 and 2016 had been milder for investment than saving.
6. The data also put shed light on that the Indian society exhibits a strong desire for a male child. It pointed out that most parents continue to have children until they get the desired number of sons. The survey further gave details of the skewed sex ratio in the country. North-eastern states consistently out-perform others in gender issues, hinterland states lag behind, while southern states do less well than their development levels would suggest.
7. Sanitation coverage in rural India increased considerably from 39 percent in 2014 to 76 percent in January 2018. With the launch of Swachh Bharat Mission (Gramin) on October 2, 2014, the sanitation coverage in rural India increased substantially. So far, 296 districts and 307,349 villages all over India have been declared Open Defecation Free (ODF).
8. India is steadily improving its performance in Science and Technology. In 2013, India ranked 6th in the world in scientific publications. Its ranking has been increasing consistently. The growth of annual publications between 2009 to 2014 was almost 14 percent. This greater than before India's share in global publications from 3.1 percent in 2009 to 4.4 percent in 2014 as per the Scopus Database.
9. India's formal non-agricultural payroll is considerably greater than what it is currently believed to be. It became evident that when formality was defined in terms of social security provisions like EPFO/ESIC, the payroll was found to be about 75 million. When formality was defined in terms of being part of the GST net, such formal sector payroll share was found to be 127 million.
10. The foreign exchange reserves grew by 14.1 percent on a year-on-year basis from end of Dec 2016 to end of Dec 2017. The forex reserves as per 2016-17 were estimated at USD 370 billion. It grew to USD 409.4 billion in 2017-18. (NT)