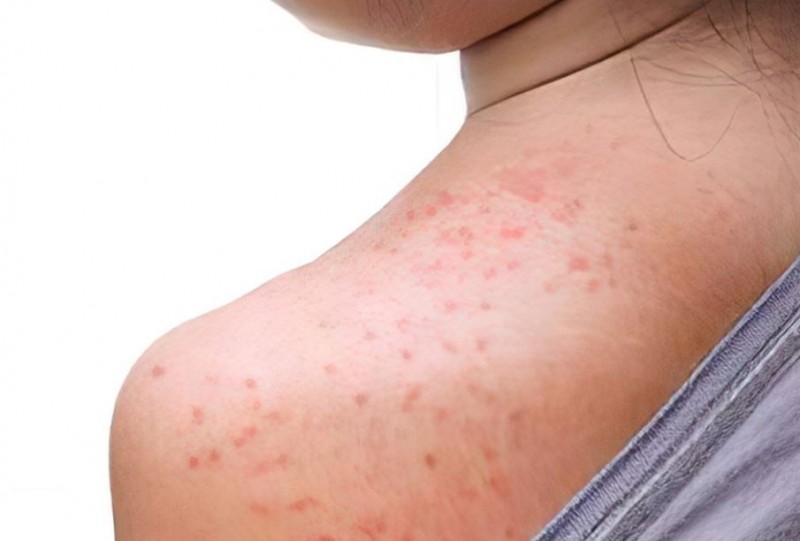
Heat rash, also known as prickly heat or miliaria, is a common dermatological condition that affects people of all ages, including adults. It occurs when sweat ducts become blocked, leading to the retention of sweat beneath the skin's surface. This blockage can result in a variety of symptoms, including redness, itching, and small, fluid-filled blisters. In this article, we will delve into the causes of heat rash in adults and explore effective methods for its prevention and treatment.
I. Causes of Heat Rash in Adults
Hot and Humid Weather:
One of the primary triggers for heat rash in adults is exposure to hot and humid weather. When the body overheats, it produces sweat as a natural cooling mechanism. However, in excessively hot and humid conditions, the sweat ducts can become overwhelmed and clogged, leading to the development of heat rash.
Tight Clothing:
Wearing tight-fitting clothing, especially during warm weather, can contribute to the development of heat rash. Tight clothes can trap sweat against the skin, making it difficult for sweat to evaporate, and increasing the likelihood of sweat duct blockage.
Physical Activity:
Engaging in vigorous physical activities, such as running or exercising in hot weather, can lead to increased sweating. This excessive sweating can exacerbate the risk of heat rash in adults, especially if clothing choices do not allow for proper ventilation.
Heavy Lotions and Creams:
The use of heavy lotions or creams on the skin can occlude sweat ducts, preventing the proper release of sweat. This is particularly relevant if these products are applied in areas prone to friction and sweat accumulation, such as the inner thighs or under the breasts.
Immobility:
Adults who are bedridden or have limited mobility may also be at risk for developing heat rash. Prolonged contact with bedding or clothing can lead to the trapping of sweat and the subsequent blockage of sweat ducts.
II. Types of Heat Rash
Heat rash can manifest in different forms, each with its own set of symptoms and characteristics. The three main types of heat rash are:
Miliaria Crystallina:
This is the mildest form of heat rash, characterized by small, clear, fluid-filled blisters that appear on the surface of the skin. These blisters are not painful and tend to burst easily. Miliaria crystallina is often seen in newborns but can affect adults in hot and humid conditions.
Miliaria Rubra:
Also known as prickly heat, miliaria rubra presents as red bumps and may cause a prickling or stinging sensation, hence the name "prickly heat." These red bumps can be itchy and are more likely to develop in areas where sweat and friction are common, such as the neck, underarms, and groin.
Miliaria Profunda:
Miliaria profunda is the least common form of heat rash and typically affects adults who have experienced recurrent episodes of heat rash. It is characterized by deeper, flesh-colored lesions that develop within the sweat ducts. These lesions are often painless but may lead to more severe discomfort and itching.
III. Prevention of Heat Rash in Adults
Preventing heat rash in adults involves taking proactive measures to reduce the risk of sweat duct blockage and overheating. Here are some effective strategies to prevent heat rash:
Stay Cool:
Avoid prolonged exposure to hot and humid conditions, especially during the hottest parts of the day. Seek shade or air-conditioned environments when necessary.
Wear Loose, Breathable Clothing:
Choose loose-fitting, lightweight clothing made from natural fabrics like cotton. These materials allow for better air circulation and help prevent sweat duct blockage.
Use Fans and Air Conditioning:
Utilize fans and air conditioning to cool indoor spaces, and consider using fans or portable air conditioning units in outdoor settings to provide relief from extreme heat.
Stay Hydrated:
Drinking plenty of water helps regulate body temperature and promotes sweating, which can help cool the body and reduce the risk of heat rash.
Shower Regularly:
Frequent showers can help remove sweat and bacteria from the skin's surface, reducing the chances of sweat duct blockage. Use mild, fragrance-free soap to avoid skin irritation.
Avoid Heavy Ointments and Creams:
During hot and humid weather, opt for lightweight moisturizers and avoid heavy lotions or creams that may clog sweat ducts.
IV. Treatment of Heat Rash in Adults
If you find yourself with heat rash, there are several steps you can take to alleviate symptoms and promote healing. Here's how to treat heat rash in adults:
Cool the Affected Area: The first step in treating heat rash is to cool down the affected area. Move to a cooler environment, take a cool shower or apply a cold, damp cloth to the rash. Avoid hot water or ice, as extreme temperatures can worsen the condition.
Keep the Area Dry: After cooling, gently pat the affected area dry with a clean towel. Avoid rubbing the skin, as this can irritate the rash further.
Loose Clothing: Wear loose-fitting clothing made of breathable fabrics to minimize friction and promote air circulation around the rash.
Calamine Lotion or Oatmeal Baths: Applying calamine lotion or taking an oatmeal bath can help soothe itching and reduce inflammation associated with heat rash.
Over-the-Counter Creams: Non-prescription hydrocortisone creams can provide relief from itching and inflammation. However, it's essential to follow the instructions on the label and consult a healthcare professional if the rash persists or worsens.
Stay Hydrated: Continue to drink plenty of water to help regulate body temperature and support the body's natural cooling mechanism.
Avoid Tight Clothing: Refrain from wearing tight or restrictive clothing that can exacerbate the rash.
Topical Antibiotics: In cases where heat rash has become infected, topical antibiotics may be prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Seek Medical Attention: If the heat rash does not improve within a few days, or if it worsens, becomes painful, or shows signs of infection (such as pus or increased redness), consult a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and treatment.
Prevent Recurrence: Once the rash has healed, take preventive measures to avoid future occurrences. Be mindful of clothing choices, maintain proper hygiene, and stay cool during hot weather.
Heat rash in adults is a common and uncomfortable condition that can be easily prevented and treated with proper care and precautions. Understanding the causes and types of heat rash is essential for taking proactive steps to reduce the risk of its occurrence. By staying cool, wearing breathable clothing, and practicing good hygiene, you can minimize the chances of experiencing heat rash. In cases where heat rash does develop, prompt and appropriate treatment can provide relief and prevent complications. Remember that if the rash persists or worsens, it's crucial to seek medical advice for a proper evaluation and treatment plan. With the right approach, you can enjoy the summer months without the discomfort of heat rash.
Your Body's Defense: 10 Ways to Boost Glutathione and Defeat Oxidative Stress