Have you ever wondered why siblings, despite sharing similar genetic material, can have different physical traits and susceptibilities to diseases? The answer lies in the intriguing field of epigenetics. Epigenetics explores how external factors can influence the activity of our genes, potentially leading to changes in our genetic expression. In this article, we will dive into the captivating world of epigenetics, uncovering how our genes can change and the implications this has for human health and development.
1. Introduction to Epigenetics
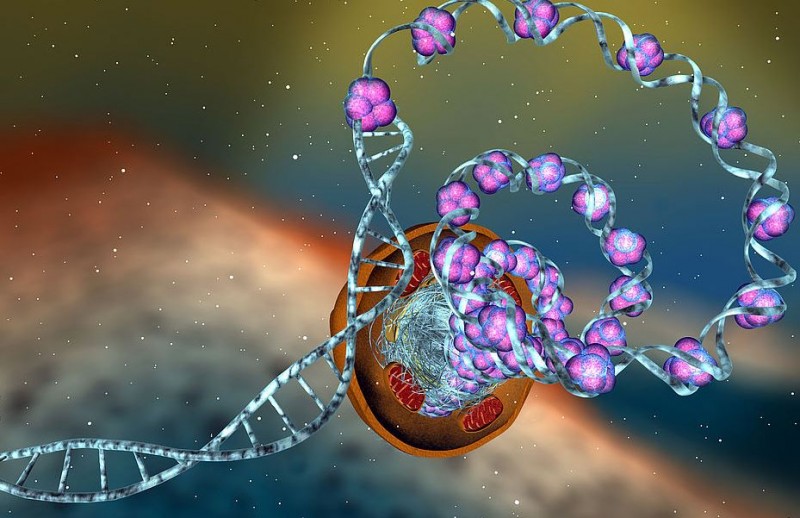
Epigenetics is a branch of genetics that explores changes in gene activity and expression that do not involve alterations to the underlying DNA sequence. Instead, epigenetic modifications can influence gene expression by turning genes on or off, affecting their accessibility to the cellular machinery responsible for gene transcription.
2. Understanding DNA and Genes
To comprehend epigenetics fully, it is essential to understand the structure and function of DNA and genes. DNA, or deoxyribonucleic acid, is the blueprint of life. It consists of a sequence of nucleotides, forming the famous double helix structure. Genes, on the other hand, are segments of DNA that encode instructions for building proteins and carrying out various biological processes.
3. Epigenetic Modifications: An Overview
Epigenetic modifications refer to chemical changes that occur on the DNA molecule or associated proteins, such as histones, without altering the DNA sequence itself. These modifications act as switches, controlling gene activity and determining whether a gene is turned on (active) or off (inactive).
4. DNA Methylation: Silencing Genes
One of the most well-studied epigenetic modifications is DNA methylation. It involves the addition of a methyl group to the DNA molecule, often leading to gene silencing. DNA methylation patterns can be inherited or acquired throughout an individual's lifetime, making them susceptible to environmental influences.
5. Histone Modification: Regulating Gene Expression
Histone modification is another crucial epigenetic mechanism. Histones are proteins that package DNA into a compact structure called chromatin. Modifications of histones, such as acetylation and methylation, can alter the chromatin structure, influencing the accessibility of genes to the cellular machinery responsible for gene expression.
6. Non-Coding RNAs: Fine-Tuning Gene Activity
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are RNA molecules that do not encode proteins but play important regulatory roles in gene expression. They can act as guides, binding to specific DNA sequences or interacting with other molecules to influence gene activity. Examples of ncRNAs include microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs).
7. Environmental Factors and Epigenetics
Environmental factors, such as diet, stress, toxins, and lifestyle choices, can impact epigenetic modifications. These factors can modify DNA methylation patterns, alter histone modifications, and affect the production of non-coding RNAs. Consequently, our environment can have a profound influence on our gene expression and overall health.
8. The Impact of Epigenetics on Development
Epigenetics plays a vital role in embryonic development and cellular differentiation. During these processes, specific genes need to be activated or silenced at precise times and locations. Epigenetic mechanisms ensure the precise orchestration of gene expression, allowing cells to differentiate into various specialized cell types that make up our body.
9. Epigenetics and Disease: Unraveling the Connections
Epigenetic changes have been implicated in the development and progression of various diseases, including cancer, neurological disorders, cardiovascular diseases, and autoimmune conditions. Understanding the underlying epigenetic alterations can provide valuable insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic strategies.
10. Epigenetics and Cancer: Insights into Tumor Formation
Cancer is characterized by uncontrolled cell growth and the formation of tumors. Epigenetic modifications can contribute to the initiation and progression of cancer by disrupting normal gene regulation. Epigenetic therapies that target these modifications show promise as potential cancer treatments.
11. Epigenetics and Aging: The Clock of Life
Aging is a complex process influenced by both genetic and environmental factors. Epigenetic changes accumulate over time, contributing to the aging process. Researchers are exploring the "epigenetic clock," a measure of biological age based on epigenetic modifications, to better understand the aging process and potential interventions to promote healthy aging.
12. The Role of Nutrition in Epigenetics
Nutrition plays a crucial role in shaping epigenetic modifications. Certain nutrients, such as folate, vitamin B12, and polyphenols, act as methyl donors or cofactors in the methylation process. A balanced diet and healthy lifestyle can support proper epigenetic regulation and reduce the risk of epigenetic-related diseases.
13. Potential Therapeutic Applications of Epigenetics
The field of epigenetics holds great promise for developing novel therapeutic approaches. Epigenetic drugs, such as DNA methyltransferase inhibitors and histone deacetylase inhibitors, are being investigated for their potential to reverse abnormal epigenetic patterns in diseases and restore normal gene expression.
14. Ethical Considerations in Epigenetic Research
As epigenetics progresses, ethical considerations come to the forefront. Privacy concerns, informed consent, and the implications of manipulating epigenetic modifications raise important ethical questions. Researchers and policymakers need to ensure that epigenetic research and applications are conducted responsibly and with consideration for potential societal impacts.
15. Conclusion
Epigenetics is a captivating field that sheds light on the intricate mechanisms by which our genes can change. Through epigenetic modifications, influenced by both genetic and environmental factors, genes can be switched on or off, affecting various aspects of human health and development. Understanding epigenetics opens up new avenues for disease prevention, personalized medicine, and therapeutic interventions.
Sports and Fitness: Benefits of Yoga for Athletes
Tecno Camon 20 Premier 5G Set to Launch in India on July 7
Automotive: The Future of Electric Vehicles and Sustainable Transportation